Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry
- PMID: 30124842
- PMCID: PMC6488973
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy271
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry
Abstract
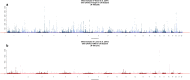
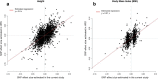
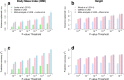
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of height and body mass index (BMI) in ∼250000 European participants have led to the discovery of ∼700 and ∼100 nearly independent single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with these traits, respectively. Here we combine summary statistics from those two studies with GWAS of height and BMI performed in ∼450000 UK Biobank participants of European ancestry. Overall, our combined GWAS meta-analysis reaches N ∼700000 individuals and substantially increases the number of GWAS signals associated with these traits. We identified 3290 and 941 near-independent SNPs associated with height and BMI, respectively (at a revised genome-wide significance threshold of P < 1 × 10-8), including 1185 height-associated SNPs and 751 BMI-associated SNPs located within loci not previously identified by these two GWAS. The near-independent genome-wide significant SNPs explain ∼24.6% of the variance of height and ∼6.0% of the variance of BMI in an independent sample from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS). Correlations between polygenic scores based upon these SNPs with actual height and BMI in HRS participants were ∼0.44 and ∼0.22, respectively. From analyses of integrating GWAS and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) data by summary-data-based Mendelian randomization, we identified an enrichment of eQTLs among lead height and BMI signals, prioritizing 610 and 138 genes, respectively. Our study demonstrates that, as previously predicted, increasing GWAS sample sizes continues to deliver, by the discovery of new loci, increasing prediction accuracy and providing additional data to achieve deeper insight into complex trait biology. All summary statistics are made available for follow-up studies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

