Blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) study
- PMID: 30125326
- PMCID: PMC6101389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202604
Blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis from the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) study.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 13;13(9):e0204340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204340. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30212585 Free PMC article.
Abstract
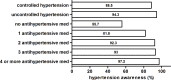
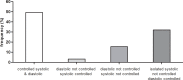
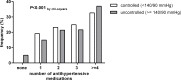
We assessed the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in patients with moderate chronic kidney disease (CKD) under nephrological care in Germany. In the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) study, 5217 patients under nephrology specialist care were enrolled from 2010 to 2012 in a prospective observational cohort study. Inclusion criteria were an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 30-60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or overt proteinuria in the presence of an eGFR>60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Office blood pressure was measured by trained study personnel in a standardized way and hypertension awareness and medication were assessed during standardized interviews. Blood pressure was considered as controlled if systolic < 140 and diastolic < 90 mmHg. In 5183 patients in whom measurements were available, mean blood pressure was 139.5 ± 20.4 / 79.3 ± 11.8 mmHg; 4985 (96.2%) of the patients were hypertensive. Awareness and treatment rates were > 90%. However, only 2456 (49.3%) of the hypertensive patients had controlled blood pressure. About half (51.0%) of the patients with uncontrolled blood pressure met criteria for resistant hypertension. Factors associated with better odds for controlled blood pressure in multivariate analyses included younger age, female sex, higher income, low or absent proteinuria, and use of certain classes of antihypertensive medication. We conclude that blood pressure control of CKD patients remains challenging even in the setting of nephrology specialist care, despite high rates of awareness and medication use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Schneider MP, Hilgers KF. What should be the goal blood pressure in nondiabetic chronic kidney disease? Current opinion in nephrology and hypertension. 2014;23(2):180–5. 10.1097/01.mnh.0000441050.36783.ba . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

