α-Synuclein interacts directly but reversibly with psychosine: implications for α-synucleinopathies
- PMID: 30127535
- PMCID: PMC6102231
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30808-9
α-Synuclein interacts directly but reversibly with psychosine: implications for α-synucleinopathies
Abstract
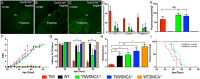
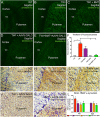
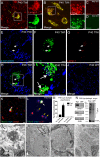
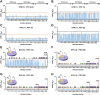
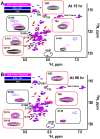
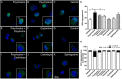
Aggregation of α-synuclein, the hallmark of α-synucleinopathies such as Parkinson's disease, occurs in various glycosphingolipidoses. Although α-synuclein aggregation correlates with deficiencies in the lysosomal degradation of glycosphingolipids (GSL), the mechanism(s) involved in this aggregation remains unclear. We previously described the aggregation of α-synuclein in Krabbe's disease (KD), a neurodegenerative glycosphingolipidosis caused by lysosomal deficiency of galactosyl-ceramidase (GALC) and the accumulation of the GSL psychosine. Here, we used a multi-pronged approach including genetic, biophysical and biochemical techniques to determine the pathogenic contribution, reversibility, and molecular mechanism of aggregation of α-synuclein in KD. While genetic knock-out of α-synuclein reduces, but does not completely prevent, neurological signs in a mouse model of KD, genetic correction of GALC deficiency completely prevents α-synuclein aggregation. We show that psychosine forms hydrophilic clusters and binds the C-terminus of α-synuclein through its amino group and sugar moiety, suggesting that psychosine promotes an open/aggregation-prone conformation of α-synuclein. Dopamine and carbidopa reverse the structural changes of psychosine by mediating a closed/aggregation-resistant conformation of α-synuclein. Our results underscore the therapeutic potential of lysosomal correction and small molecules to reduce neuronal burden in α-synucleinopathies, and provide a mechanistic understanding of α-synuclein aggregation in glycosphingolipidoses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests, except for Dr Ernesto R. Bongarzone, who is a consultant for Lysosomal Therapeutics, Inc. Lysosomal Therapeutics Inc. did not play a role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, preparation of the manuscript, or financial support in the form of authors’ salaries and/or research materials.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

