Extramedullary plasmacytoma of the larynx: Literature review and report of a case who subsequently developed acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 30127889
- PMCID: PMC6096153
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8992
Extramedullary plasmacytoma of the larynx: Literature review and report of a case who subsequently developed acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
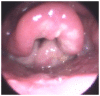
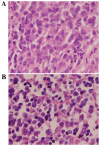
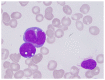
Extramedullary plasmacytoma (EMP) of the larynx is an extremely rare plasma cell neoplasm outside of the bone marrow, which has not been previously well characterized. A case of laryngeal EMP who developed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following treatment is described in the present study, as well as an extensive review of the relevant literature. An electronic literature search was performed in PubMed and all pertinent case reports and series in the English language from 1948-October 2017 were identified. A total of 99 cases including the present case were available for review. The mean age of the included patients was 53 years. Supraglottis was the most frequently involved site. The most common treatment modality was radiotherapy alone (n=41; 43%), followed by a combination of surgery and radiotherapy, then surgery alone. However, for cases published in recent years, the most common treatment modality was surgically based treatment. Overall the treatment outcome was favorable, as a total of 84% of patients were alive after a mean follow-up of 60 months. However, EMP outcomes for patients with cervical lymphadenopathy or multiple sites involvement were unfavorable with >40% of patients relapsing or developing metastasis during the limited follow-up period. A total of 6 subjects developed multiple myeloma and 1 patient converted to AML. The present study provides important insights on the treatment of EMP, which is a rare disease. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of a patient with laryngeal EMP who developed AML following treatment. It is recommended that secondary myeloid neoplasm should be considered besides multiple myeloma during the follow-up period.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; extramedullary plasmacytoma; larynx; multiple myeloma; outcomes; sequelae; treatment modality.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
