Development and evaluation of a CEACAM6-targeting theranostic nanomedicine for photoacoustic-based diagnosis and chemotherapy of metastatic cancer
- PMID: 30128051
- PMCID: PMC6096393
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.25131
Development and evaluation of a CEACAM6-targeting theranostic nanomedicine for photoacoustic-based diagnosis and chemotherapy of metastatic cancer
Abstract
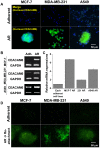
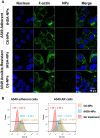
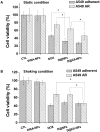
Metastasis is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. A number of chemotherapeutic and early diagnosis strategies, including nanomedicine, have been developed to target metastatic tumor cells. However, simultaneous inhibition and imaging of metastasis is yet to be fully achieved. Methods: To overcome this limitation, we have developed human serum albumin-based nanoparticles (tHSA-NPs) with photoacoustic imaging capability, which target carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6). CEACAM6 is highly expressed in metastatic anoikis-resistant tumor cells. Results:In vitro, the CEACAM6-targeting tHSA-NPs efficiently targeted CEACAM6-overexpressing metastatic anoikis-resistant tumor cells. In vivo, CEACAM6-targeting tHSA-NPs administered intravenously to BALB/c nude mice efficiently inhibited lung metastasis in circulating anoikis-resistant tumor cells compared to the controls. In addition, anoikis-resistant tumor cells can be successfully detected by photoacoustic imaging, both in vitro and in vivo, using the intrinsic indocyanine green-binding affinity of albumin. Conclusion: In summary, the CEACAM6-targeting albumin-based nanoparticles allowed the delivery of drugs and photoacoustic imaging to metastatic anoikis-resistant tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Based on the expression of CEACAM6 in a variety of tumors, CEACAM6-targeting nanomedicine might be used to target various types of metastatic tumor cells.
Keywords: CEACAM6; anoikis resistance; metastasis; nanomedicine; photoacoustic imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Mar;64(3):27. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5615. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38240103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoacoustic-based nanomedicine for cancer diagnosis and therapy.J Control Release. 2015 Apr 10;203:118-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25701310
-
Chemotherapeutic drug-photothermal agent co-self-assembling nanoparticles for near-infrared fluorescence and photoacoustic dual-modal imaging-guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy.J Control Release. 2017 Jul 28;258:95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 May 10. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28501673
-
CEACAM6 gene silencing impairs anoikis resistance and in vivo metastatic ability of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2004 Jan 15;23(2):465-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207036. Oncogene. 2004. Retraction in: Oncogene. 2023 Mar;42(12):939. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02625-6. PMID: 14724575 Retracted.
-
Ultrasound nanotheranostics in fighting cancer: Advances and prospects.Cancer Lett. 2020 Feb 1;470:204-219. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.034. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31790760 Review.
Cited by
-
Anoikis-Associated Lung Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 30;14(19):4791. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194791. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems in Breast Cancer Therapy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;12(17):2948. doi: 10.3390/nano12172948. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36079985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Functions and Identification of Novel Biomarker Expressed on the Surface of Breast Cancer-Derived Cancer Stem Cells via Proteomic Analysis.Mol Cells. 2020 Apr 30;43(4):384-396. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2020.2230. Mol Cells. 2020. PMID: 32235022 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor Cells: Does Ion Transport Contribute to Intravascular Survival, Adhesion, Extravasation, and Metastatic Organotropism?Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;182:139-175. doi: 10.1007/112_2021_68. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35137308 Review.
-
The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Mar;64(3):27. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5615. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38240103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mehlen P, Puisieux A. Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:449–58. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS, Kobayashi H, Graham CH. Intrinsic or acquired drug-resistance and metastasis - are they linked phenotypes. J Cell Biochem. 1994;56:37–47. - PubMed
-
- Voulgari A, Pintzas A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796:75–90. - PubMed
-
- Lee K, Lee H, Bae KH, Park TG. Heparin immobilized gold nanoparticles for targeted detection and apoptotic death of metastatic cancer cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31:6530–6. - PubMed
-
- Yang F, Jin C, Yang D, Jiang YJ, Li J, Di Y. et al. Magnetic functionalised carbon nanotubes as drug vehicles for cancer lymph node metastasis treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:1873–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

