C797S Resistance: The Undruggable EGFR Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
- PMID: 30128066
- PMCID: PMC6088362
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00314
C797S Resistance: The Undruggable EGFR Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Abstract
The first evidence of osimertinib resistance mediated by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation C797S was reported three years ago. Since then, no major breakthroughs have been achieved to target the clinically relevant mutant variant that impedes covalent bond formation with irreversible EGFR inhibitors. Although several biochemically active compounds have been described, only a few inhibitors that potently act on the cellular level or in vivo have been introduced so far. Herein, we give an overview of current approaches in the field and highlight the challenges that need to be addressed in future research projects to overcome the C797S-mediated drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
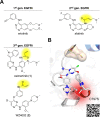
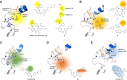
References
-
- Chen Y.; Wu J.; Wang A.; Qi Z.; Jiang T.; Chen C.; Zou F.; Hu C.; Wang W.; Wu H.; Hu Z.; Wang W.; Wang B.; Wang L.; Ren T.; Zhang S.; Liu Q.; Liu J. Discovery of N-(5-((5-chloro-4-((2-(isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)-4-met hoxy-2-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)phenyl)acrylamide (CHMFL-ALK/EGFR-050) as a potent ALK/EGFR dual kinase inhibitor capable of overcoming a variety of ALK/EGFR associated drug resistant mutants in NSCLC. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 674–697. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

