Mechanisms Underlying Muscle Protein Imbalance Induced by Alcohol
- PMID: 30130465
- PMCID: PMC6377942
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064642
Mechanisms Underlying Muscle Protein Imbalance Induced by Alcohol
Abstract
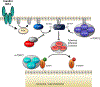
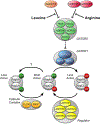
Both acute intoxication and longer-term cumulative ingestion of alcohol negatively impact the metabolic phenotype of both skeletal and cardiac muscle, independent of overt protein calorie malnutrition, resulting in loss of skeletal muscle strength and cardiac contractility. In large part, these alcohol-induced changes are mediated by a decrease in protein synthesis that in turn is governed by impaired activity of a protein kinase, the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR). Herein, we summarize recent advances in understanding mTOR signal transduction, similarities and differences between the effects of alcohol on this central metabolic controller in skeletal muscle and in the heart, and the effects of acute versus chronic alcohol intake. While alcohol-induced alterations in global proteolysis via activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway are equivocal, emerging data suggest alcohol increases autophagy in muscle. Further studies are necessary to define the relative contributions of these bidirectional changes in protein synthesis and autophagy in the etiology of alcoholic myopathy in skeletal muscle and the heart.
Keywords: alcoholic myopathy; amino acids; autophagy; mTOR; protein synthesis; translational control; ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Bento CF, Renna M, Ghislat G, Puri C, Ashkenazi A, et al. 2016. Mammalian autophagy: How does It work? Annu Rev Biochem 85: 685–713 - PubMed
-
- Bernal CA, Vazquez JA, Adibi SA. 1993. Leucine metabolism during chronic ethanol consumption. Metabolism: clinical and experimental 42: 1084–6 - PubMed
-
- Buerger C, DeVries B, Stambolic V. 2006. Localization of Rheb to the endomembrane is critical for its signaling function. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 344: 869–80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

