Abemaciclib Is Active in Preclinical Models of Ewing Sarcoma via Multipronged Regulation of Cell Cycle, DNA Methylation, and Interferon Pathway Signaling
- PMID: 30131386
- PMCID: PMC6279561
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1256
Abemaciclib Is Active in Preclinical Models of Ewing Sarcoma via Multipronged Regulation of Cell Cycle, DNA Methylation, and Interferon Pathway Signaling
Abstract
Purpose: Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a rare and highly malignant cancer that occurs in the bone and surrounding tissue of children and adolescents. The EWS/ETS fusion transcription factor that drives ES pathobiology was previously demonstrated to modulate cyclin D1 expression. In this study, we evaluated abemaciclib, a small-molecule CDK4 and CDK6 (CDK4 and 6) inhibitor currently under clinical investigation in pediatric solid tumors, in preclinical models of ES.
Experimental design: Using Western blot, high-content imaging, flow cytometry, ELISA, RNA sequencing, and CpG methylation assays, we characterized the in vitro response of ES cell lines to abemaciclib. We then evaluated abemaciclib in vivo in cell line-derived xenograft (CDX) and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse models of ES as either a monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy.
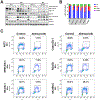
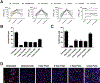
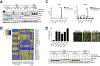
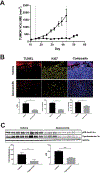
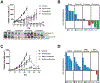
Results: Abemaciclib induced quiescence in ES cell lines via a G1 cell-cycle block, characterized by decreased proliferation and reduction of Ki-67 and FOXM1 expression and retinoblastoma protein (RB) phosphorylation. In addition, abemaciclib reduced DNMT1 expression and promoted an inflammatory immune response as measured by cytokine secretion, antigen presentation, and interferon pathway upregulation. Single-agent abemaciclib reduced ES tumor volume in preclinical mouse models and, when given in combination with doxorubicin or temozolomide plus irinotecan, durable disease control was observed.
Conclusions: Collectively, our data demonstrate that the antitumor effects of abemaciclib in preclinical ES models are multifaceted and include cell-cycle inhibition, DNA demethylation, and immunogenic changes.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
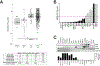
References
-
- Cesari M, Righi A, Cevolani L, Palmerini E, Vanel D, Donati DM, et al. Ewing sarcoma in patients over 40 years of age: a prospective analysis of 31 patients treated at a single institution. Tumori 2016;102:481–7 - PubMed
-
- Esiashvili N, Goodman M, Marcus RB, Jr. Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over the past 3 decades: Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results data. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008;30:425–30 - PubMed
-
- Rainusso N, Wang LL, Yustein JT. The adolescent and young adult with cancer: state of the art -- bone tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 2013;15:296–307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

