Executive Function Predicting Longitudinal Change in Type 1 Diabetes Management During the Transition to Emerging Adulthood
- PMID: 30131398
- PMCID: PMC6196825
- DOI: 10.2337/dc18-0351
Executive Function Predicting Longitudinal Change in Type 1 Diabetes Management During the Transition to Emerging Adulthood
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to examine 1) whether teens' glycemic control and adherence to type 1 diabetes treatment regimen worsen during the transition from late adolescence to emerging adulthood, and 2) whether teens' executive function (EF), as measured by performance and self-reported problems with EF, is predictive of these changes (after controlling for general intelligence).
Research design and methods: High school seniors with type 1 diabetes (N = 236; mean age 17.74 years) were assessed at three yearly time points. At baseline, during the senior year of high school, participants completed a self-report measure of problems with EF and performance-based measures of EF and general intelligence (IQ). Glycemic control was determined on the basis of results collected from HbA1c assay kits, and teens reported their adherence at all three time points.
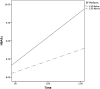
Results: HbA1c increased significantly across the three time points and adherence declined. EF performance was not associated with adherence or HbA1c at baseline, nor with changes in adherence over time. However, better EF performance predicted slower increases in HbA1c over time (i.e., slope) while controlling for IQ. Teens' self-reported problems with EF were associated with worse glycemic control and poorer adherence at baseline (i.e., intercept), but they did not predict changes in either HbA1c or adherence over time (i.e., slope).
Conclusions: Abilities involved in performance on EF tests may be one resource for maintaining better glycemic control during the transition to emerging adulthood. Assessment of such EF abilities may allow for the identification of individuals who are most at risk for deterioration of glycemic control during this transition.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Weissberg-Benchell J, Wolpert H, Anderson BJ. Transitioning from pediatric to adult care: a new approach to the post-adolescent young person with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2441–2446 - PubMed
-
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al.; T1D Exchange Clinic Network . Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2015;38:971–978 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous