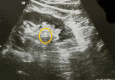
Multiple renal calculi due to hypercalcaemia induced by over-the-counter vitamin D intoxication
- PMID: 30131404
- PMCID: PMC6109724
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225849
Multiple renal calculi due to hypercalcaemia induced by over-the-counter vitamin D intoxication
Abstract
Renal stone disease is a common and painful condition. Even though it is rarely fatal, patients describe it as the worst pain in their life. While dietary calcium may decrease the risk of stone formation, patients on supplemental calcium are at higher risk. Moreover, patients with diabetes are more prone to develop renal calculi. Hypervitaminosis D is a rare cause of hypercalcaemia. This is a case of an elderly diabetic man who developed multiple calcium oxalate renal stones due to hypercalcaemia following calcium-vitamin D supplementation.
Keywords: calcium and bone; diabetes; renal system; vitamins and supplements.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bringhurst FR, Demay MB, Krane SM, et al. . Bone and mineral metabolism in healthy and disease : Kasper F, Hauser L, Jameson L, Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 19th edn New York, USA: McGraw Hill Education, 2015:2463–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical