High miR-718 Suppresses Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) Expression and Correlates to Unfavorable Prognosis in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 30131483
- PMCID: PMC6116637
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909527
High miR-718 Suppresses Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) Expression and Correlates to Unfavorable Prognosis in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
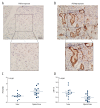
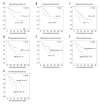
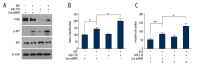
BACKGROUND Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a kind of phosphatase which has been demonstrated to suppress progression of gastric cancer. Many micro-RNAs (miRNAs), such as miR-106b, miR-93, and miR-200c, could inhibit expression of PTEN in cell lines; and many miRNAs including miR-21, miR-22, miR-18a, and miR-222 are related to the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer. However, among these miRNAs, the clinical significance of miR-718 has not yet been elucidated. MATERIAL AND METHODS The expression of PTEN and miR-718 in 141 gastric cancer tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry and quantitative real-time PCR respectively. The correlation between PTEN, miR-718, and the clinicopathological factors was analyzed by χ² test. The prognostic significance of PTEN and miR-718 was evaluated by univariate and multivariate analysis. Luciferase reporter assay was performed to evaluate the regulation of PTEN by miR-718. The effect of miR-718 on gastric cancer proliferation and invasion was investigated by MTT assay and Transwell assay. RESULTS Low expression of PTEN and high expression of miR-718 were both significantly associated with unfavorable prognosis, and both were identified as biomarkers predicting poorer prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Increased miR-718 expression could decrease PTEN expression, thus enhancing phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling. Moreover, the abilities of proliferation and invasion of gastric cells transfected with miR-718 were promoted significantly compared with those transfected with control miRNA. CONCLUSIONS Low expression of PTEN and increased expression of miR-718 in gastric cancer tissues were both independent unfavorable prognostic factors of gastric cancer. Upregulation of miR-718 could increase PI3K/Akt signaling by directly downregulating PTEN, thus promoting the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-106b promotes pituitary tumor cell proliferation and invasion through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting PTEN.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13469-13477. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5155-2. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27465551
-
miR-21 Inhibitors Modulate Biological Functions of Gastric Cancer Cells via PTEN/PI3K/mTOR Pathway.DNA Cell Biol. 2018 Jan;37(1):38-45. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.3922. Epub 2017 Nov 29. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29185784
-
Micro-RNA 205-5p is Involved in the Progression of Gastric Cancer and Targets Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN) in SGC-7901 Human Gastric Cancer Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 24;25:6367-6377. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915970. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31444971 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-132 promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of human pancreatic carcinoma by inhibition of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;148:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 28941804 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in gastric cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2019 Mar;41(3):1439-1454. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.6962. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30628706 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical crosstalk between microRNAs and gastric cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5187. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biochemical and clinical implications of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten in different cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 15;11(12):5833-5855. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35018228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Next-Generation Sequencing of Plasma Exosome-Derived microRNAs and Target Gene Analysis with a Microarray Database of Thermally Injured Skins: Identification of Blood-to-Tissue Interactions at Early Burn Stage.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Dec 10;14:6783-6798. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S343956. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34916825 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Angiogenesis and Its Biomarkers in Development of Targeted Tumor Therapies.Stem Cells Int. 2024 Jan 4;2024:9077926. doi: 10.1155/2024/9077926. eCollection 2024. Stem Cells Int. 2024. PMID: 38213742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-23a Promotes Angiogenesis by Targeting PTEN.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 13;10:326. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00326. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32232005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen PH, Giraud J, Chambonnier L, et al. Characterization of biomarkers of tumorigenic and chemoresistant cancer stem cells in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(6):1586–97. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97. - PubMed
-
- Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, et al. Characterization of microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2007;67(6):2456–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

