Reliability of two different protocols used for intentional re-implantation of periodontally hopeless teeth
- PMID: 30131630
- PMCID: PMC6077966
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_170_18
Reliability of two different protocols used for intentional re-implantation of periodontally hopeless teeth
Abstract
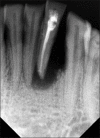
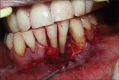
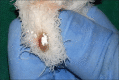
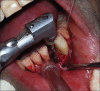
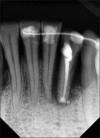
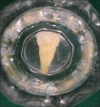
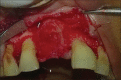
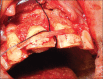
Intentional re-implantation is the careful removal and re-insertion of an endodontically treated tooth performed with an attempt to preserve the natural dentition and patients' esthetic concerns. Its limited success rate and a possibility to obtain undesirable outcomes such as root resorption and ankylosis of the tooth restrict its clinical use to be attempted only as a last option after routine procedures. A vast array of procedures have been performed till date with inconsistent results due to lack of analogous protocols followed. Regardless of having a controversial background behind its success in periodontally compromised teeth, this procedure raises a hope to avoid unwarranted natural tooth loss. Performing each step with precision governs the success of the treatment. This case report demonstrates two different techniques with an interdisciplinary approach assessed over 1 year each.
Keywords: Ankylosis; intentional re-implantation; interdisciplinary approach; periodontally compromised teeth; root resorption; tooth loss.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


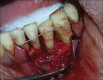
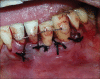

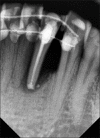
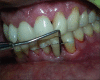


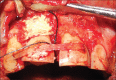
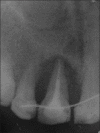
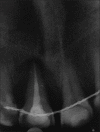
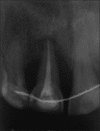
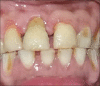
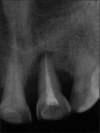

References
-
- Grossman LI. Intentional replantation of teeth. J Am Dent Assoc. 1966;72:1111–8. - PubMed
-
- Rouhani A, Javidi B, Habibi M, Jafarzadeh H. Intentional replantation: A procedure as a last resort. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2011;12:486–92. - PubMed
-
- Cho SY, Lee SJ, Kim E. Clinical outcomes after intentional replantation of periodontally involved teeth. J Endod. 2017;43:550–5. - PubMed
-
- Demiralp B, Nohutçu RM, Tepe DI, Eratalay K. Intentional replantation for periodontally involved hopeless teeth. Dent Traumatol. 2003;19:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Baykara M, Eratalay K. Replantation in cases with advanced periodontal destruction. J Hacettepe Fac Dent. 1995;19:124–8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

