NLRC3 negatively regulates CD4+ T cells and impacts protective immunity during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- PMID: 30133544
- PMCID: PMC6122840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007266
NLRC3 negatively regulates CD4+ T cells and impacts protective immunity during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Abstract
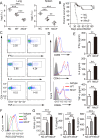
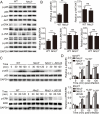
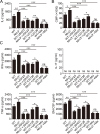
NLRC3, a member of the NLR family, has been reported as a negative regulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in innate immune cells. However, the direct role of NLRC3 in modulation of CD4+ T-cell responses in infectious diseases has not been studied. In the present study, we showed that NLRC3 plays an intrinsic role by suppressing the CD4+ T cell phenotype in lung and spleen, including differentiation, activation, and proliferation. NLRC3 deficiency in CD4+ T cells enhanced the protective immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Finally, we demonstrated that NLRC3 deficiency promoted the activation, proliferation, and cytokine production of CD4+ T cells via negatively regulating the NF-κB and MEK-ERK signaling pathways. This study reveals a critical role of NLRC3 as a direct regulator of the adaptive immune response and its protective effects on immunity during M. tuberculosis infection. Our findings also suggested that NLRC3 serves as a potential target for therapeutic intervention against tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

