Interleukin-17-producing γδ T (γδ17) cells in inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 30133701
- PMCID: PMC6231014
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12993
Interleukin-17-producing γδ T (γδ17) cells in inflammatory diseases
Abstract
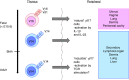
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine and is involved in the development of many diseases. Recent studies have revealed that IL-17-producing γδ T cells (γδ17 cells) in addition to IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells [T helper type 17 (Th17) cells] are often the main producers of IL-17 in mouse models of inflammatory diseases. γδ T cells are functionally committed during intra-thymic differentiation. γδ thymocytes capable of producing IL-17, which express the transcription factor retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan receptor γt and the signature cytokine receptor IL-23R, leave the thymus, and produce IL-17 rapidly by the stimulation with IL-1β and IL-23 in the periphery. Therefore, γδ17 cells play important roles in the early phase of host defence against pathogens and in inflammatory diseases. γδ T cells that can produce IL-17 are also increased in the skin of patients with psoriasis and in peripheral blood of patients with ankylosing sclerosis. Indeed, the therapy targeting IL-17 has been approved or is in clinical trials, and proved to be very efficient to treat psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing sclerosis. In this review, we discuss recent knowledge about the pathophysiological function of γδ17 cells in infection and inflammatory diseases and therapeutic advances targeting IL-17.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammatory disease; pathogen clearance.
© 2018 The Authors. Immunology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S, Nakae S. Functional specialization of interleukin‐17 family members. Immunity 2011; 34:149–62. - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M. Interleukin 17 is a chief orchestrator of immunity. Nat Immunol 2017; 18:612–21. - PubMed
-
- Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Nagai T, Kadoki M, Nambu A, Komiyama Y et al Differential roles of interleukin‐17A and ‐17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 2009; 30:108–19. - PubMed
-
- Saijo S, Ikeda S, Yamabe K, Kakuta S, Ishigame H, Akitsu A et al Dectin‐2 recognition of alpha‐mannans and induction of Th17 cell differentiation is essential for host defense against Candida albicans . Immunity 2010; 32:681–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

