Site-Specific Glycosylation of Virion-Derived HIV-1 Env Is Mimicked by a Soluble Trimeric Immunogen
- PMID: 30134158
- PMCID: PMC6113929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.080
Site-Specific Glycosylation of Virion-Derived HIV-1 Env Is Mimicked by a Soluble Trimeric Immunogen
Abstract
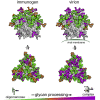
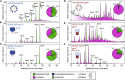
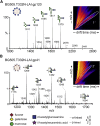
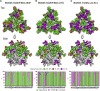
Many broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) against HIV-1 recognize and/or penetrate the glycan shield on native, virion-associated envelope glycoprotein (Env) spikes. The same bnAbs also bind to recombinant, soluble trimeric immunogens based on the SOSIP design. While SOSIP trimers are close structural and antigenic mimics of virion Env, the extent to which their glycan structures resemble ones on infectious viruses is undefined. Here, we compare the overall glycosylation of gp120 and gp41 subunits from BG505 (clade A) virions produced in a lymphoid cell line with those from recombinant BG505 SOSIP trimers, including CHO-derived clinical grade material. We also performed detailed site-specific analyses of gp120. Glycans relevant to key bnAb epitopes are generally similar on the recombinant SOSIP and virion-derived Env proteins, although the latter do contain hotspots of elevated glycan processing. Knowledge of native versus recombinant Env glycosylation will guide vaccine design and manufacturing programs.
Keywords: HIV; envelope glycoprotein; glycosylation; mass spectrometry.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Binley J.M., Sanders R.W., Clas B., Schuelke N., Master A., Guo Y., Kajumo F., Anselma D.J., Maddon P.J., Olson W.C., Moore J.P. A recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein complex stabilized by an intermolecular disulfide bond between the gp120 and gp41 subunits is an antigenic mimic of the trimeric virion-associated structure. J. Virol. 2000;74:627–643. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

