Dysequilibrium of the PTH-FGF23-vitamin D axis in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis; a longitudinal study
- PMID: 30134801
- PMCID: PMC6016878
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-018-0028-3
Dysequilibrium of the PTH-FGF23-vitamin D axis in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis; a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Parathyroid glands of people with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) fail to respond to low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) and low serum calcium, which are stimuli for parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion. This led us to hypothesise: that there is suppression of PTH in RRMS due to higher than normal serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23). We therefore sought evidence for dysregulation of the PTH-FGF23-vitamin D axis in RRMS.
Methods: Longitudinal study (winter to summer) with fasting venepunctures. For RRMS subjects who recruited a healthy control (HC) friend, pairs analyses were performed. For each pair, the within-pair difference of the variable of interest was calculated (RRMS minus HC). Then, the median of the differences from all pairs was compared against a median of zero (Wilcoxon) and the 95% confidence interval of that median difference (CI) was calculated (Sign Test).
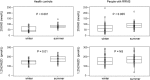
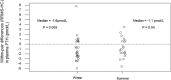
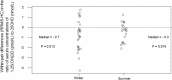
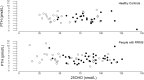
Results: RRMS had lower winter PTH than HC, P = 0.005, (CI -2.4 to 0.5 pmol/L, n = 28 pairs), and lower summer PTH, P = 0.04, (CI -1.8 to 0.5, n = 21 pairs). Lower PTH associates physiologically with lower intact FGF23 (iFGF23), yet RRMS had higher iFGF23 than HC in winter, P = 0.04, (CI -3 to 15 pg/mL, n = 28 pairs) and iFGF23 levels comparable to HC in summer, P = 0.14, (CI -5 to 13, n = 21 pairs). As PTH stimulates and FGF23 reduces, renal 1-alpha hydroxylase enzyme activity, which synthesises serum 1,25-dihyroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) from serum 25OHD, we examined the ratio of serum 1,25(OH)2D to serum 25OHD. In winter, this ratio was lower in RRMS versus HC, P = 0.013, (CI -1.2 to - 0.3, n = 28 pairs).
Conclusions: This study revealed a dysequilibrium of the PTH-FGF23-vitamin D axis in RRMS, with lower plasma PTH, higher plasma iFGF23 and a lower serum 1,25(OH)2D to 25OHD ratio in RRMS compared with HC subjects. This dysequilibrium is consistent with the study hypothesis that in RRMS there is suppression of the parathyroid glands by inappropriately high plasma concentrations of iFGF23. Studying the basis of this dysequilibrium may provide insight into the pathogenesis of RRMS.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor 23; Multiple sclerosis; Parathyroid hormone; Vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committees of Melbourne Health and Eastern Health, Victoria. All subjects provided written informed consent.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 3. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1994. pp. 96–97.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

