Usefulness of Automated Latex Turbidimetric Rapid Plasma Reagin Test for Diagnosis and Evaluation of Treatment Response in Syphilis in Comparison with Manual Card Test: a Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 30135229
- PMCID: PMC6204675
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01003-18
Usefulness of Automated Latex Turbidimetric Rapid Plasma Reagin Test for Diagnosis and Evaluation of Treatment Response in Syphilis in Comparison with Manual Card Test: a Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
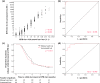
The usefulness of an automated latex turbidimetric rapid plasma reagin (RPR) assay, compared to the conventional manual card test (serial 2-fold dilution method), for the diagnosis of syphilis and evaluation of treatment response remains unknown. We conducted (i) a cross-sectional study and (ii) a prospective cohort study to elucidate the correlation between automated and manual tests and whether a 4-fold decrement is a feasible criterion for successful treatment with the automated test, respectively, in HIV-infected patients, from October 2015 to November 2017. Study i included 518 patients. The results showed strong correlation between the two tests (r = 0.931; P < 0.001). With a manual test titer of ≥1:8 plus a positive Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA) test as the reference standard for diagnosis, the optimal cutoff value for the automated test was 6.0 RPR units (area under the curve [AUC], 0.998), with positive predictive value (PPV) of 92.5% and negative predictive value (NPV) of 99.4%. Study ii enrolled 66 men with syphilis. Their RPR values were followed up until after 12 months of treatment. At 12 months, 77.3% and 78.8% of the patients achieved a 4-fold decrement in RPR titer by the automated and manual test, respectively. The optimal decrement rate in RPR titer by the automated test for a 4-fold decrement by manual card test was 76.54% (AUC, 0.96) (PPV, 96.1%; NPV, 80.0%). The automated RPR test is a good alternative to the manual test for the diagnosis of syphilis and evaluation of treatment response and is more rapid and can handle more specimens than the manual test without interpersonal variation in interpretation.
Keywords: automated test; manual; rapid plasma reagin; syphilis; treatment response.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of an automated rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test with the conventional RPR card test in syphilis testing.BMJ Open. 2014 Dec 31;4(12):e005664. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005664. BMJ Open. 2014. PMID: 25552608 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Manual and Fully Automated AIX1000 Rapid Plasma Reagin Assays for Laboratory Diagnosis of Syphilis.J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Jul 26;56(8):e00214-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00214-18. Print 2018 Aug. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29618500 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the fully automated AIX1000 rapid plasma reagin system compared to a manual plasma reagin testing method for the diagnosis of syphilis.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Aug;97(4):115081. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115081. Epub 2020 May 15. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32534240
-
The Laboratory Diagnosis of Syphilis.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Sep 20;59(10):e0010021. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00100-21. Epub 2021 May 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33980644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The serological dilemma: rethinking syphilis treatment evaluation.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025 Feb-Apr;23(2-4):181-195. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2025.2467646. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025. PMID: 39945601 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in rapid plasma reagin titers in patients with syphilis before and after treatment: A retrospective cohort study in an HIV/AIDS referral hospital in Tokyo.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 28;18(9):e0292044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292044. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37768989 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 17 serological treponemal and nontreponemal assays for syphilis: A retrospective cohort study.Pract Lab Med. 2022 Sep 29;32:e00302. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2022.e00302. eCollection 2022 Nov. Pract Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 36217361 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral tonsillitis due to primary syphilis with gram-negative corkscrew-like spirochaetes confirmed by Gram stain of pus.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Feb 17;17(2):e258549. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-258549. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38367986 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Tolerability of Oral Amoxicillin in Pregnant Women with Active Syphilis, Japan, 2010-2018.Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Jun;26(6):1192-1200. doi: 10.3201/eid2606.191300. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32441638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, Wijesooriya NS, Unemo M, Low N, Stevens G, Gottlieb S, Kiarie J, Temmerman M. 2015. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 10:e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2016. Syphilis—2015 STD surveillance. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA: https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats15/syphilis.htm Accessed 24 February 2018.
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Japan. 2016. Infectious diseases weekly report 2016, vol 18, p 8–9. National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan: https://www0.niid.go.jp/niid/idsc/idwr/IDWR2016/idwr2016-48.pdf Accessed 24 February 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

