Plasma microRNA markers of upper limb recovery following human stroke
- PMID: 30135469
- PMCID: PMC6105620
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31020-5
Plasma microRNA markers of upper limb recovery following human stroke
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Plasma microRNA markers of upper limb recovery following human stroke.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 7;10(1):2484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58943-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32034207 Free PMC article.
Abstract
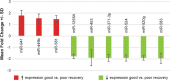
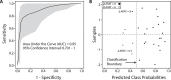
Preclinical investigators have implicated several microRNAs as regulators of gene expression promoting neural plasticity following experimental stroke in rodent models. Our goal was to determine whether similar microRNAs might be identifiable in plasma of humans with variable recovery from stroke. Plasma was collected 19 days post-stroke from 27 participants with mild-moderate upper extremity impairment enrolled in the Critical Periods After Stroke Study (CPASS). MicroRNA expression was assessed using TaqMan microRNA assays. Good clinical recovery was defined as ≥6 point change in the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) score from baseline to 6 months, with 22 subjects showing good and 5 showing poor recovery. When comparing the good versus poor recovery groups, six microRNAs showed significantly increased expression - miR-371-3p, miR-524, miR-520g, miR-1255A, miR-453, and miR-583, while 3 showed significantly decreased expression - miR-941, miR-449b, and miR-581. MiR-371-3p and miR-941 have previously been associated with neural repair mechanisms; none of the significant microRNAs have previously been associated with stroke. The 9 microRNAs converge on pathways associated with axonal guidance, developmental biology, and cancer. We conclude that plasma microRNAs may be informative regarding human neural repair mechanisms during stroke recovery and probably differ from those seen in experimental stroke models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kosik KS. The neuronal microRNA system. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 2006;7:911–920. - PubMed
-
- Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:509–524. - PubMed
-
- Valadi H, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:654–659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR031975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000101/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)/International
- KL2 TR001432/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA051008/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA051008/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

