Architecture of the native major royal jelly protein 1 oligomer
- PMID: 30135511
- PMCID: PMC6105727
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05619-1
Architecture of the native major royal jelly protein 1 oligomer
Abstract
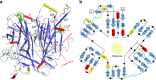
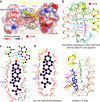
Honeybee caste development is nutritionally regulated by royal jelly (RJ). Major royal jelly protein 1 (MRJP1), the most abundant glycoprotein among soluble royal jelly proteins, plays pivotal roles in honeybee nutrition and larvae development, and exhibits broad pharmacological activities in humans. However, its structure has long remained unknown. Herein, we identify and report a 16-molecule architecture of native MRJP1 oligomer containing four MRJP1, four apisimin, and eight unanticipated 24-methylenecholesterol molecules at 2.65 Å resolution. MRJP1 has a unique six-bladed β-propeller fold with three disulfide bonds, and it interacts with apisimin mainly by hydrophobic interaction. Every four 24-methylenecholesterol molecules are packaged by two MRJP1 and two apisimin molecules. This assembly dimerizes to form an H-shaped MRJP14-apisimin4-24-methylenecholesterol8 complex via apisimin in a conserved and pH-dependent fashion. Our findings offer a structural basis for understanding the pharmacological effects of MRJPs and 24-methylenecholesterol, and provide insights into their unique physiological roles in bees.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

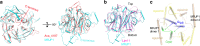


Similar articles
-
Characterizing the Structure and Oligomerization of Major Royal Jelly Protein 1 (MRJP1) by Mass Spectrometry and Complementary Biophysical Tools.Biochemistry. 2017 Mar 21;56(11):1645-1655. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00020. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28252287 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of native glycolipoprotein filaments in honeybee royal jelly.Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 8;11(1):6267. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20135-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33293513 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel hypocholesterolemic protein, major royal jelly protein 1, derived from royal jelly.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 21;9(8):e105073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105073. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25144734 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and function of the major royal jelly proteins of the honeybee (Apis mellifera) as members of the yellow gene family.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2014 May;89(2):255-69. doi: 10.1111/brv.12052. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2014. PMID: 23855350 Review.
-
Royal Jelly: An ancient remedy with remarkable antibacterial properties.Microbiol Res. 2016 Nov;192:130-141. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Microbiol Res. 2016. PMID: 27664731 Review.
Cited by
-
Sterol and lipid metabolism in bees.Metabolomics. 2023 Aug 29;19(9):78. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-02039-1. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 37644282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol-soluble proteins from the royal jelly of Xinjiang black bees.Protein Sci. 2021 Feb;30(2):291-296. doi: 10.1002/pro.3985. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33131155 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Effect of Honey-Derived Exosomes Containing Antimicrobial Peptides Against Oral Streptococci.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jul 20;16:4891-4900. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S315040. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34321877 Free PMC article.
-
An Evolutionary Perspective of Dopachrome Tautomerase Enzymes in Metazoans.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jun 28;10(7):495. doi: 10.3390/genes10070495. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31261784 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Insects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5753. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065753. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simuth J. Some properties of the main protein of honeybee (Apis mellifera) royal jelly. Apidologie. 2001;32:69–80. doi: 10.1051/apido:2001112. - DOI
-
- Tamura S, Kono T, Harada C, Yamaguchi K, Moriyama T. Estimation and characterisation of major royal jelly proteins obtained from the honeybee Apis merifera. Food Chem. 2009;114:1491–1497. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.058. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

