Binge Drinking among adolescents is related to the development of Alcohol Use Disorders: results from a Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 30135518
- PMCID: PMC6105639
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-29311-y
Binge Drinking among adolescents is related to the development of Alcohol Use Disorders: results from a Cross-Sectional Study
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Binge Drinking among adolescents is related to the development of Alcohol Use Disorders: results from a Cross-Sectional Study.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 16;8(1):15476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33705-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30327506 Free PMC article.
Abstract
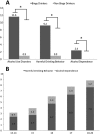
Binge drinking (BD) is a common pattern of alcohol consumption among adolescents. At present few data are available on the possible relationship between BD and alcohol use disorders (AUD) in adolescents. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of BD and relationship between BD behavior and AUD among adolescents. A total of 2704 students attending 10 purposively selected high schools from three Italian provinces were surveyed. Questionnaires regarding socio-demographic data, pattern and amount of alcohol intake, smoking habits, use of illicit drugs, and physical activity were administered. AUD and affective disorders were also evaluated. Alcohol intake was reported by 2126 participants; 1278 reported at least one episode BD in the last year and 715 in the last month. A diagnosis of AUD was made in 165 adolescents. The prevalence of AUD was higher in adolescents that reported BD behavior than in those that did not report BD (11.6% vs 0.9%, respectively; p < 0.0001). Logistic regression showed a positive relationship between a diagnosis of AUD and BD behavior (OR 9.6; 95% CI 4.7-22·9; p < 0.0001). In conclusion alcohol consumption with the pattern of BD among adolescents is highly related to development of AUD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Global health risks. Geneva, World Health Organization. (http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/...) (2011).
-
- WHO. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical