MicroRNA miR-509 Regulates ERK1/2, the Vimentin Network, and Focal Adhesions by Targeting Plk1
- PMID: 30135525
- PMCID: PMC6105636
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-30895-8
MicroRNA miR-509 Regulates ERK1/2, the Vimentin Network, and Focal Adhesions by Targeting Plk1
Abstract
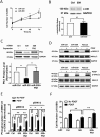
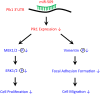
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) has been implicated in mitosis, cytokinesis, and proliferation. The mechanisms that regulate Plk1 expression remain to be elucidated. It is reported that miR-100 targets Plk1 in certain cancer cells. Here, treatment with miR-100 did not affect Plk1 protein expression in human airway smooth muscle cells. In contrast, treatment with miR-509 inhibited the expression of Plk1 in airway smooth muscle cells. Exposure to miR-509 inhibitor enhanced Plk1 expression in cells. Introduction of miR-509 reduced luciferase activity of a Plk1 3'UTR reporter. Mutation of miR-509 targeting sequence in Plk1 3'UTR resisted the reduction of the luciferase activity. Furthermore, miR-509 inhibited the PDGF-induced phosphorylation of MEK1/2 and ERK1/2, and cell proliferation without affecting the expression of c-Abl, a tyrosine kinase implicated in cell proliferation. Moreover, we unexpectedly found that vimentin filaments contacted paxillin-positive focal adhesions. miR-509 exposure inhibited vimentin phosphorylation at Ser-56, vimentin network reorganization, focal adhesion formation, and cell migration. The effects of miR-509 on ERK1/2 and vimentin were diminished in RNAi-resistant Plk1 expressing cells treated with miR-509. Taken together, these findings unveil previously unknown mechanisms that miR-509 regulates ERK1/2 and proliferation by targeting Plk1. miR-509 controls vimentin cytoskeleton reorganization, focal adhesion assembly, and cell migration through Plk1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ammit AJ, Panettieri RA., Jr. Airway smooth muscle cell hyperplasia: a therapeutic target in airway remodeling in asthma? Prog.Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Orsini MJ, et al. MAPK superfamily activation in human airway smooth muscle: mitogenesis requires prolonged p42/p44 activation. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:L479–L488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-130304/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/International
- R01 HL113208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110951/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-113208/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/International
- HL-110951/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

