Effect of switching to teneligliptin from other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glucose control and renoprotection in type 2 diabetes patients with diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 30136384
- PMCID: PMC6497591
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12917
Effect of switching to teneligliptin from other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glucose control and renoprotection in type 2 diabetes patients with diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Aims/introduction: The objective of the present study was to elucidate the effect of switching to teneligliptin from other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors on glucose control and renoprotection in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Materials and methods: The present study was a single-arm, open-label, observational study. A total of 23 patients, who had urinary albumin/creatinine ratios (UACR) ≥30 mg/gCr in their first urine in the early morning, and received other DPP-4 inhibitors and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, switched to teneligliptin 20 mg/day. After switching to teneligliptin for 24 weeks, we evaluated changes in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose levels, plasma DPP-4 activity and UACR.
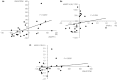
Results: HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose and UACR values showed no significant change after 24 weeks compared with baseline. However, plasma DPP-4 activity was significantly reduced after 24 weeks (0.57 ± 0.26 nmol/min/mL, P = 0.012, vs baseline), compared with baseline (1.49 ± 1.73 nmol/min/mL), and there was a positive relationship between the change rate of plasma DPP-4 activity (Δ%DPP-4) for 24 weeks and the levels of plasma DPP-4 activity (r = -0.5997, P = 0.0025) and fasting plasma glucose (r = -0.4235, P = 0.0440) at baseline. Additionally, the Δ%DPP-4 for 24 weeks was significantly correlated to the change rate of UACR (r = 0.556, P = 0.0059). However, there was no relationship between Δ%DPP-4 and ΔHbA1c (amount of HbA1c change).
Conclusions: Switching to teneligliptin from other DPP-4 inhibitors for 24 weeks reduces plasma DPP-4 activity, which is associated with a reduction in albuminuria, independent of the change in glucose levels, in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with diabetic kidney disease.
Keywords: Diabetic kidney disease; Plasma DPP-4 activity; Teneligliptin.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved glycemic control with teneligliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on hemodialysis: Evaluation by continuous glucose monitoring.J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(8):1310-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.07.002. Epub 2015 Jul 3. J Diabetes Complications. 2015. PMID: 26298521 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 24-week multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016 May;18(5):528-32. doi: 10.1111/dom.12631. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016. PMID: 26749529 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin added to glimepiride in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with an open-label, long-term extension.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 May;16(5):418-25. doi: 10.1111/dom.12235. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24205974 Clinical Trial.
-
Teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2013 Oct;49(10):615-29. doi: 10.1358/dot.2013.49.10.2035882. Drugs Today (Barc). 2013. PMID: 24191255 Review.
-
Teneligliptin : expectations for its pleiotropic action.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;16(3):417-26. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2015.1000301. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25597385 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Nov 2;13:4113-4121. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S267994. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33173319 Free PMC article.
-
Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise.J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Apr;12(4):537-545. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13389. Epub 2020 Sep 20. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 32810383 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Teneligliptin in Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity: An In-Vitro Study.Cureus. 2022 Apr 6;14(4):e23871. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23871. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35530894 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 5;10(2):246. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020246. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Nutritive, Mineral, and Antinutritive Composition of Musa sinensis L. (Banana) and Musa paradisiaca L. (Plantain) Fruit Compartments.Plants (Basel). 2019 Dec 12;8(12):598. doi: 10.3390/plants8120598. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31842474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, et al Severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta‐analysis with bias analysis. BMJ 2013; 347: f4533. - PubMed
-
- Howse PM, Chibrikova LN, Twells LK, et al Safety and efficacy of incretin‐based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and CKD: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2016; 68: 733–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

