Amelioration of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by combined RNA interference of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and YKL-40
- PMID: 30138439
- PMCID: PMC6107246
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202797
Amelioration of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by combined RNA interference of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and YKL-40
Abstract
To test the hypothesis that combined RNA interference (RNAi) of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) and YKL-40 is superior to RNAi of Lp-PLA2 or YKL-40 alone in ameliorating atherosclerosis. A total of 120 apolipoprotein E-deficient mice (apoE-/- mice) were randomly divided into five groups, including the vehicle alone, scrambled RNAi, Lp-PLA2 RNAi, YKL-40 RNAi, and combined Lp-PLA2 and YKL-40 RNAi groups. Constrictive collars were used to induce plaque formation. Lp-PLA2 RNAi and YKL-40 RNAi viral suspensions were transduced into carotid plaques of the mice. Carotid plaques were harvested for histological analysis four weeks after viral vector transduction. Inflammatory gene expression in the plasma and atherosclerotic plaques was determined by ELISA and real-time PCR. Four weeks after RNAi, the serum concentration and plaque mRNA expression of Lp-PLA2 and YKL-40 were remarkably attenuated, leading to reduced inflammatory gene expression. Plaques from the Lp-PLA2 or YKL-40 RNAi group showed lower lipid content, higher collagen content, increased fibrous cap thickness, and lower mRNA expressions of MCP-1 and MMP-8 than than those in the vehicle and scramble groups. When compared with the isolated Lp-PLA2 or YKL-40 RNAi group, the combined Lp-PLA2 and YKL-40 RNAi group exhibited higher collagen content and fibrous cap thickness, and lower lipid content and local inflammation. The beneficial effects of RNAi were independent of the plasma lipoprotein profile. Combined RNAi of Lp-PLA2 and YKL-40 is superior to RNAi of Lp-PLA2 or YKL-40 alone in ameliorating atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
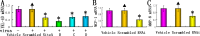




References
-
- Zhang H, Zhang JY, Sun TW, Shen DL, He F, Dang YH, et al. Amelioration of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by inhibition of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2. Clin Invest Med. 2013;36:E32–E41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

