Changing resource landscapes and spillover of henipaviruses
- PMID: 30138535
- PMCID: PMC6778453
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.13910
Changing resource landscapes and spillover of henipaviruses
Abstract
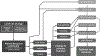
Old World fruit bats (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae) provide critical pollination and seed dispersal services to forest ecosystems across Africa, Asia, and Australia. In each of these regions, pteropodids have been identified as natural reservoir hosts for henipaviruses. The genus Henipavirus includes Hendra virus and Nipah virus, which regularly spill over from bats to domestic animals and humans in Australia and Asia, and a suite of largely uncharacterized African henipaviruses. Rapid change in fruit bat habitat and associated shifts in their ecology and behavior are well documented, with evidence suggesting that altered diet, roosting habitat, and movement behaviors are increasing spillover risk of bat-borne viruses. We review the ways that changing resource landscapes affect the processes that culminate in cross-species transmission of henipaviruses, from reservoir host density and distribution to within-host immunity and recipient host exposure. We evaluate existing evidence and highlight gaps in knowledge that are limiting our understanding of the ecological drivers of henipavirus spillover. When considering spillover in the context of land-use change, we emphasize that it is especially important to disentangle the effects of habitat loss and resource provisioning on these processes, and to jointly consider changes in resource abundance, quality, and composition.
Keywords: habitat loss; henipavirus; land-use change; resource provisioning; spillover.
© 2018 New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Heywood VH & Stuart SN. 1992. “Tropical deforestation and species extinction.” Whitmore TC and Sauer JA, Eds.: London: Chapman and Hall.
-
- Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, et al. 1997. Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 277: 504–9. - PubMed
-
- Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, et al. 1997. Human Domination of Earth’s Ecosystems. Science (80-. ) 277: 494–499.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

