Disinfection by Ozone Microbubbles Can Cause Morphological Change of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis Spores
- PMID: 30140187
- PMCID: PMC6097823
- DOI: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.11.2017.0234
Disinfection by Ozone Microbubbles Can Cause Morphological Change of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis Spores
Abstract
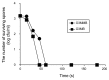
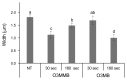
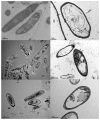
To investigate the difference in the disinfectant efficiency of ozone microbubbles (O3MB) and ozone millibubbles (O3MMB), the morphological change of the treated Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis spores was observed with scanning and transmission electron microscopies (SEM and TEM). The disinfectant efficiency of O3MB on F. oxysporum f. sp. melonis spores was greater than that of O3MMB. On observation with SEM, it was revealed that morphological change of F. oxysporum f. sp. melonis spores was caused by O3MB and O3MMB, and damage to the spore surfaces by O3MB occurred sooner than that by O3MMB. On observation with TEM, it was furthermore confirmed that F. oxysporum f. sp. melonis spores treated with O3MB induced wavy deformation of cell membrane and the intracellular change different from that with O3MMB. Therefore, the greater disinfection efficiency of O3MB was suggested to be caused due to the function of the MB in addition to the oxidative power of O3.
Keywords: Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis spores; disinfection; ozone microbubbles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Temperature effect on Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. melonis survival during horticultural waste composting.J Appl Microbiol. 2003;94(3):475-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.01854.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12588556
-
Activity of Haliscosamine against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. melonis: in vitro and in vivo analysis.Springerplus. 2015 Jan 13;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-0797-x. eCollection 2015. Springerplus. 2015. PMID: 25625038 Free PMC article.
-
A New Race of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis Causing Fusarium Wilt of Muskmelon in the Central Valley of California.Plant Dis. 1997 Sep;81(9):1095. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.1997.81.9.1095A. Plant Dis. 1997. PMID: 30861975
-
Polygenic Inheritance of Partial Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis Race 1.2 in Melon.Phytopathology. 2004 Dec;94(12):1331-6. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.12.1331. Phytopathology. 2004. PMID: 18943703
-
Resistance risk assessment of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis against phenamacril, a myosin inhibitor.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018 May;147:127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2017.09.014. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29933982
References
-
- Bando K, Kawano M, Kuroda Y, Kusakari S, Yamasaki M, Maeda T, Kourai H. Effect of silver-supported photocatalytic sterilization, yield, quality, and nutrient element concentrations in the tomato grown under rockwool culture. Hortic Res (Japan) 2008;7:309–315. doi: 10.2503/hrj.7.309. (in Japanese). - DOI
-
- Chu LB, Xing XH, Yu AF, Sun XL, Jurcik B. Enhanced treatment of practical textile wastewater by microbubble ozonation. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2008;86:389–393. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2008.02.005. - DOI
-
- Chuajedton A, Nuanaon N, Uthaibutra J, Whangchai K. Ozone microbubbles disinfection technique to inactivate penicillium digitatum in suspension. Acta Hortic. 2015;1088:355–358. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1088.60. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

