Gambogic acid inhibits LPS-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory cytokine production mainly through suppression of the p38 pathway
- PMID: 30140411
- PMCID: PMC6098961
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.23897.5995
Gambogic acid inhibits LPS-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory cytokine production mainly through suppression of the p38 pathway
Abstract
Objectives: In traditional Chinese medicine, gamboge can detoxify bodies, kill parasites, and act as a hemostatic agent. Recent studies have demonstrated that gambogic acid (GBA) suppressed inflammation in arthritis, and also presented antitumor effect. Thus, this study investigated the new biological properties of GBA on macrophages.
Materials and methods: RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with GBA at different concentrations (10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320 nM) for 24 hrs, and then cell viability was measured using Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assays. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β were determined using ELISA kits and qPCR. Then nitrite concentration was calculated according to a standard curve. At last, the effect of GBA on MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways was assessed by western blot and luciferase reporter gene assay.
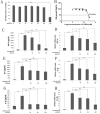
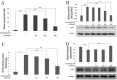
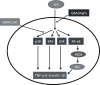
Results: GBA (IC50: 260 nM) suppressed the TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β expression induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in RAW 264.7 cells. The expression of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β decreased to 30-50% and 70-75% in the high-dose (160 nM) and low-dose (40 and 80 nM) GBA groups, respectively. Furthermore, the nitric oxide (NO) production and the activation of NF-κB, ERK, and JNK pathways were significantly reduced in high-dose (160 nM) GBA only, while p38 pathway was inhibited at both low (40 and 80 nM) and high (160 nM) concentration of GBA.
Conclusion: These data suggested that GBA inhibited LPS-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β mainly through the suppression of the p38 pathway.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory agents; Gambogic acid; MAPK; NF-κB; RAW 264.7 cells; p38.
Figures

References
-
- Bartold PM, Cantley MD, Haynes DR. Mechanisms and control of pathologic bone loss in periodontitis. Periodontology. 2010;53:55–69. - PubMed
-
- Adams DO, Hamilton TA. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. - PubMed
-
- Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 2008;42:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Kim KN, Heo SJ, Yoon WJ, Kang SM, Ahn G, Yi TH, et al. Fucoxanthin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of NF-kappaB and MAPKs in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 2647 macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;649:369–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
