A systematic review of associations between non-communicable diseases and socioeconomic status within low- and lower-middle-income countries
- PMID: 30140435
- PMCID: PMC6076564
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.08.020409
A systematic review of associations between non-communicable diseases and socioeconomic status within low- and lower-middle-income countries
Abstract
Background: Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the leading cause of death globally. Eighty-two percent of premature NCD deaths occur within low- and lower middle-income countries (LLMICs). Research to date, largely drawn from high-income countries, suggests that disadvantaged and marginalized groups have a higher NCD burden, but there has been a dearth of research studying this relationship within LLMICs. The purpose of this systematic review is to map the literature on evidence from LLMICs on the socio-economic status (SES) gradient of four particular NCDs: cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases.
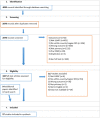
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive literature search for primary research published between 1 January 1990 and 27 April 2015 using six bibliographic databases and web resources. We included studies that reported SES and morbidity or mortality from cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory diseases within LLMICs.
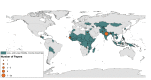
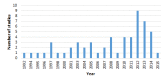
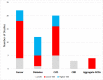
Results: Fifty-seven studies from 17 LLMICs met our inclusion criteria. Fourteen of the 18 papers that reported significant associations between cancer and SES suggested that low SES groups had the highest cancer risk. Eleven of 15 papers reporting significant relationships between CVD and SES suggested that low SES groups have higher risk. In contrast, seven of 12 papers reporting significant findings related to diabetes found that higher SES groups had higher diabetes risk. We identified just three studies on the relationship between chronic respiratory diseases and SES; none of them reported significant findings.
Conclusions: Only 17 of the 84 LLMICs were represented, highlighting the need for more research on NCDs within these countries. The majority of studies were medium to high quality cross-sectional studies. When we restricted our analyses to high quality studies only, for both cancer and cardiovascular disease more than half of studies found a significantly higher risk for those of lower SES. The opposite was true for diabetes, whilst there was a paucity of high quality research on chronic respiratory disease. Development programmes must consider health alongside other aims and NCD prevention interventions must target all members of the population.
Systematic review registration number: Prospero: CRD42015020169.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Dr Wickramasinghe reports other from World Health Organization during the conduct of the study; Dr Mikkelsen reports personal fees from World Health Organization, during the conduct of the study. The authors has completed the Unified Competing Interest form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author) and declare no other competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations. Report of the Director-General of the World Health Organization on the Prevention and control of non-communicable diseases. Document A/R68/650. 2013.
-
- Mendis S. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. 2014. Available: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/. Accessed: 23 May 2018.
-
- United Nations. Outcome document of the high-level meeting of the General Assembly on the comprehensive review and assessment of the progress achieved in the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases. A/RES/68/300. 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
