Comparative Evaluation of Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Along With Scalp Block on Haemodynamic and Postoperative Recovery for Chronic Subdural Haematoma Evacuation Under Monitored Anaesthesia Care
- PMID: 30140501
- PMCID: PMC5858890
- DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2018.16878
Comparative Evaluation of Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Along With Scalp Block on Haemodynamic and Postoperative Recovery for Chronic Subdural Haematoma Evacuation Under Monitored Anaesthesia Care
Abstract
Objective: Chronic subdural haematoma (CSDH) is a common neurosurgical problem, and treatment includes evacuation of the haematoma by burr hole drainage. Commonly, these procedures are performed under local anaesthesia, general anaesthesia or, recently, with monitored anaesthesia care (MAC). We compared dexmedetomidine- and propofol-based sedation along with scalp nerve block for burr hole evacuation of CSDH.
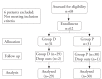
Methods: In this prospective randomised study, 62 patients were divided into the following two groups of 31 patients each: Group D and Group P. Group D received dexmedetomidine 1 μg kg-1 over 10 minutes as a loading dose, followed by 0.2-0.7 μg kg-1 hr-1. Group P received propofol 1 mg kg-1 over 10 minutes as a loading dose, followed by 1-3 mg kg-1 hr-1. The heart rate (HR) and blood pressure were measured at different intervals. The recovery parameter and satisfaction score were also recorded.
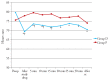
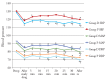
Results: There were no significant differences noted in the demographic profile. A significant decrease in HR compared to preoperative value was seen in Group D compared to Group P. Blood pressure values were statistically significantly lower in both study groups, compared to preoperative values during the whole procedure and after surgery (p<0.05). Time to achieve modified Aldrete score of 9-10 was not significantly different between the groups (p=0.354). Surgeon satisfaction was significantly better in Group D compared to Group P (p<0.05), but patient satisfaction was similar between the groups (p=0.364).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine-based sedation compared to propofol, along with scalp block for MAC in patients undergoing burr hole evacuation of CSDH is associated with haemodynamic stability and greater surgeon satisfaction.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; chronic subdural haematoma; monitored anaesthesia care; propofol.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dexmedetomidine versus Propofol Along with Scalp Block for Chronic Subdural Haematoma Evacuation Under Monitored Anaesthesia Care: Which is Better?Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019 Feb;47(1):79-80. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2018.13914. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019. PMID: 31276117 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Guzel A, Kaya S, Ozkan U, Ufuk Aluclu M, Ceviz A, Belen D. Surgical treatment of chronic subdural haematoma under monitored anaesthesia care. Swiss Med Wkly. 2008;138:398–403. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Feng L, Bai F, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Ren C. The Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine vs. Sufentanil in Monitored Anesthesia Care during Burr-Hole Surgery for Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Retrospective Clinical Trial. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:410. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00410. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
