Evaluation of a Combined Reflectance Confocal Microscopy-Optical Coherence Tomography Device for Detection and Depth Assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 30140851
- PMCID: PMC6179925
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.2446
Evaluation of a Combined Reflectance Confocal Microscopy-Optical Coherence Tomography Device for Detection and Depth Assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
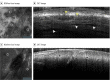
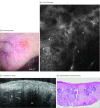
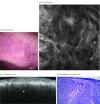
Importance: The limited tissue sampling of a biopsy can lead to an incomplete assessment of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) subtypes and depth. Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) combined with optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging may enable real-time, noninvasive, comprehensive three-dimensional sampling in vivo, which may improve the diagnostic accuracy and margin assessment of BCCs.
Objective: To determine the accuracy of a combined RCM-OCT device for BCC detection and deep margin assessment.
Design, setting, and participants: This pilot study was carried out on 85 lesions from 55 patients referred for physician consultation or Mohs surgery at Memorial Sloan Kettering Skin Cancer Center in Hauppauge, New York. These patients were prospectively and consecutively enrolled in the study between January 1, 2017, and December 31, 2017. Patients underwent imaging, with the combined RCM-OCT probe, for previously biopsied, histopathologically confirmed BCCs and lesions clinically or dermoscopically suggestive of BCC. Only patients with available histopathologic examination after imaging were included.
Main outcomes and measures: Improvements in sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy for BCC using the combined RCM-OCT probe as well as the correlation between OCT-estimated depth and histopathologically measured depth were investigated.
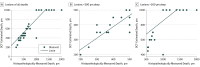
Results: In total, 85 lesions from 55 patients (27 [49%] were female and 28 [51%] were male with a median [range] age of 59 [21-90] years) were imaged. Imaging was performed on 25 previously biopsied and histopathologically confirmed BCCs and 60 previously nonbiopsied but clinically or dermoscopically suspicious lesions. Normal skin and BCC features were correlated and validated with histopathologic examination. In previously biopsied lesions, residual tumors were detected in 12 of 25 (48%) lesions with 100% sensitivity (95% CI, 73.5%-100%) and 23.1% specificity (95% CI, 5.0%-53.8%) for combined RCM-OCT probe. In previously nonbiopsied and suspicious lesions, BCCs were diagnosed in 48 of 60 (80%) lesions with 100% sensitivity (95% CI, 92.6%-100%) and 75% specificity (95% CI, 42.8%-94.5%). Correlation was observed between depth estimated with OCT and depth measured with histopathologic examination: the coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.75 (R = 0.86; P < .001) for all lesions, 0.73 (R = 0.85; P < .001) for lesions less than 500 μm deep, and 0.65 (R = 0.43; P < .001) for lesions greater than 500 μm deep.
Conclusions and relevance: Combined RCM-OCT imaging may be prospectively used to comprehensively diagnose lesions suggestive of BCC and triage for treatment. Further validation of this device must be performed on a larger cohort.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presurgical evaluation of basal cell carcinoma using combined reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography: A prospective study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Apr;82(4):962-968. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.10.028. Epub 2019 Oct 18. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31634517 Free PMC article.
-
Management of complex head-and-neck basal cell carcinomas using a combined reflectance confocal microscopy/optical coherence tomography: a descriptive study.Arch Dermatol Res. 2021 Apr;313(3):193-200. doi: 10.1007/s00403-020-02037-6. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021. PMID: 32020324 Free PMC article.
-
Angulated small nests and cords: Key diagnostic histopathologic features of infiltrative basal cell carcinoma can be identified using integrated reflectance confocal microscopy-optical coherence tomography.J Cutan Pathol. 2021 Jan;48(1):53-65. doi: 10.1111/cup.13871. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Cutan Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32989842 Free PMC article.
-
Reflectance confocal microscopy for diagnosing keratinocyte skin cancers in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 4;12(12):CD013191. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013191. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30521687 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography for diagnosing skin cancer in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 4;12(12):CD013189. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013189. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30521690 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research Techniques Made Simple: Emerging Imaging Technologies for Noninvasive Optical Biopsy of Human Skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2022 May;142(5):1243-1252.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.01.016. J Invest Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35461534 Free PMC article.
-
Incompletely excised lentigo maligna melanoma is associated with unpredictable residual disease: clinical features and the emerging role of reflectance confocal microscopy.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Oct;34(10):2280-2287. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16272. Epub 2020 Mar 15. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 32030827 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Multimodal Imaging and Its Role in Diagnosing Skin Lesions in Dermatology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2025 Jul 8. doi: 10.1007/s40257-025-00958-4. Online ahead of print. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40627274
-
In vivo tumor immune microenvironment phenotypes correlate with inflammation and vasculature to predict immunotherapy response.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 9;13(1):5312. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32738-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36085288 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Role of High-frequency Ultrasound in Assessing Dermatological Manifestations in Autoimmune Skin Diseases.Acta Derm Venereol. 2022 Aug 24;102:adv00765. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v102.1969. Acta Derm Venereol. 2022. PMID: 36000997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trakatelli M, Morton C, Nagore E, et al. ; BCC Subcommittee of the Guidelines Committee of the European Dermatology Forum . Update of the European guidelines for basal cell carcinoma management. Eur J Dermatol. 2014;24(3):312-329. - PubMed
-
- Kauvar AN, Cronin T Jr, Roenigk R, Hruza G, Bennett R; American Society for Dermatologic Surgery . Consensus for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment: basal cell carcinoma, including a cost analysis of treatment methods. Dermatol Surg. 2015;41(5):550-571. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000000296 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

