Level of Compliance in Orthokeratology
- PMID: 30142103
- PMCID: PMC6116798
- DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000516
Level of Compliance in Orthokeratology
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the level of compliance with orthokeratology (ortho-k) guidelines and the main behaviors of poor compliance to guide clinical care.
Methods: A questionnaire was sent to ortho-k patients in the Eye Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (EHWMU) in Mainland China who were prescribed ortho-k lenses after January 2013 and have worn ortho-k lenses for more than 1 year to determine the compliance rate for eight wear and care behaviors. Follow-up visit compliance was then investigated among these patients using a retrospective survey.
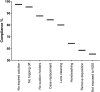
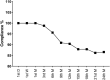
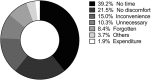
Results: A total of 1,500 questionnaires were distributed, and 405 patients responded. The mean age of the patients was 13.1±3.9 years (range 9-22 years); 60.5% of the patients were female, and 98.3% were younger than 18 years. The full compliance rate was 14.1%, the compliance rate for wear and care behaviors was 18.5%, and the compliance rate for follow-up visits was 63.3%. The three highest noncompliance categories for wear and care behaviors were exposure to nonsterile solution, not removing lens depositions according to the eye care practitioners' (ECPs) recommendations and inadequate hand washing. No correlation was observed between the compliance for wear and care behaviors and age, sex, and wearing experience. The follow-up visit compliance rate significantly decreased from the third month to the ninth month. The common reasons for discontinuing follow-up were lack of time, no symptoms, and inconvenience.
Conclusions: The level of compliance with ortho-k lens wear in Mainland China is not high, necessitating ECPs to stress to patients the details of wear and care behaviors, especially avoiding exposing lenses to nonsterile solution. Improving monitoring of follow-up visits, particularly within the first 9 months of wearing ortho-k lenses, is needed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of patient compliance in orthokeratology and analysis of influencing factors: a cross-sectional study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov 16;21(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02148-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34784895 Free PMC article.
-
Compliance with orthokeratology care among parents of young children in Taiwan.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021 Oct;44(5):101427. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2021.02.013. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021. PMID: 33622606
-
An assessment of consecutively presenting orthokeratology patients in a Hong Kong based private practice.Clin Exp Optom. 2003 Sep;86(5):331-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2003.tb03129.x. Clin Exp Optom. 2003. PMID: 14558855
-
Analysis of parental decisions to use orthokeratology for myopia control in successful wearers.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021 Jan;41(1):3-12. doi: 10.1111/opo.12744. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021. PMID: 33063901 Review.
-
How Can We Better Inform Patients of the Importance of Contact Lens Compliance?: Current Perspectives.Clin Optom (Auckl). 2024 Nov 2;16:267-286. doi: 10.2147/OPTO.S405204. eCollection 2024. Clin Optom (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 39507399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An investigation into the causes of abnormal waste of Ortho-K lenses.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 15;10:981573. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.981573. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36045728 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Satisfaction, Compliance and Side Effects among Long-Term Orthokeratology Wearers.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 15;11(14):4126. doi: 10.3390/jcm11144126. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35887890 Free PMC article.
-
Compliance with contact lens care and factors driving noncompliance in health-care students in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr 22;36(1):75-82. doi: 10.4103/SJOPT.SJOPT_202_21. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35971483 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of patient compliance in orthokeratology and analysis of influencing factors: a cross-sectional study.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov 16;21(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02148-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34784895 Free PMC article.
-
Review on the Myopia Pandemic: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention.Mo Med. 2021 Mar-Apr;118(2):156-163. Mo Med. 2021. PMID: 33840860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hiraoka T, Kakita T, Okamoto F, et al. Long-term effect of overnight orthokeratology on axial length elongation in childhood myopia: A 5-year follow-up study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012;53:3913–3919. - PubMed
-
- Xie P, Guo X. Chinese experiences on orthokeratology. Eye Contact Lens 2016;42:43–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical