Differential effects of diesel exhaust particles on T cell differentiation and autoimmune disease
- PMID: 30143013
- PMCID: PMC6109291
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-018-0271-3
Differential effects of diesel exhaust particles on T cell differentiation and autoimmune disease
Abstract
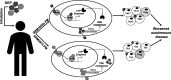
Background: Exposure to particulate matter (PM) has been associated with increased incidence and severity of autoimmune disease. Diesel PM is primarily composed of an elemental carbon core and adsorbed organic compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and contributes up to 40% of atmospheric PM. The organic fraction (OF) of PM excludes all metals and inorganics and retains most organic compounds, such as PAHs. Both PM and OF increase inflammation in vitro and aggravate autoimmune disease in humans. PAHs are known aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) ligands. The AHR modulates T cell differentiation and effector function in vitro and in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a murine model of autoimmune disease. This study aims to identify whether the total mass or active components of PM are responsible for activating pathways associated with exposure to PM and autoimmune disease. This study tests the hypothesis that active components present in diesel PM and their OF enhance effector T cell differentiation and aggravate autoimmune disease.
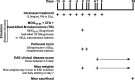
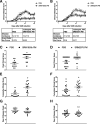
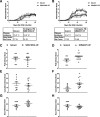
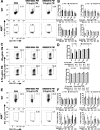
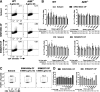
Results: Two different diesel samples, each characterized for their components, were tested for their effects on autoimmunity. Both diesel PM enhanced effector T cell differentiation in an AHR-dose-dependent manner and suppressed regulatory T cell differentiation in vitro. Both diesel PM aggravated EAE in vivo. Fractionated diesel OFs exhibited the same effects as PM in vitro, but unlike PM, only one diesel OF aggravated EAE. Additionally, both synthetic PAH mixtures that represent specific PAHs found in the two diesel PM samples enhanced Th17 differentiation, however one lost this effect after metabolism and only one required the AHR.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that active components of PM and not total mass are driving T cell responses in vitro, but in vivo the PM matrix and complex mixtures adsorbed to the particles, not just the OF, are contributing to the observed EAE effects. This implies that examining OF alone may not be sufficient in vivo. These data further suggest that bioavailability and metabolism of organics, especially PAHs, may have an important role in vivo.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Autoimmune disease; Cytochrome P450; Diesel exhaust particles; Metabolism; Particulate matter; T cell differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal studies were performed in accordance with protocols approved by the School of Medicine and Public Health Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Institute HE . State of global air 2018. Boston: Health Effects Institute; 2018.
-
- Lerner A, Jeremias P, Matthias T. The world incidence and prevalence of autoimmune diseases is increasing. Int J Celiac Dis. 2015;3(4):151–5. 10.12691/ijcd-3-4-8.
-
- Health NIo: Progress in autoimmune disease research. National Institute of Health; 2005.
-
- Miller FW, Alfredsson L, Costenbader KH, Kamen DL, Nelson LM, Norris JM, et al. Epidemiology of environmental exposures and human autoimmune diseases: findings from a National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences expert panel workshop. J Autoimmun. 2012;39(4):259–71. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22739348. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

