[Changes in the tumor necrosis factor-α level after an ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block in elderly patients with a hip fracture]
- PMID: 30143316
- PMCID: PMC9391823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjan.2018.03.004
[Changes in the tumor necrosis factor-α level after an ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block in elderly patients with a hip fracture]
Abstract
Background and objectives: An ultrasound guided femoral nerve block is an established analgesic method in patients with a hip fracture. Elevated cytokine levels correlate with poor patient outcomes after surgery. Hence, the aim of the study was to describe the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α after an ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block in elderly patients having a femoral neck fracture.
Methods: A total of 32 patients were allocated into two treatment groups: 16 patients (femoral nerve block group; ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block with up to 20 mL of 0.3 mL.kg−1 of 0.5% bupivacaine and intravenous tramadol) and 16 patients (standard management group; up to 3 mL of 0.9% saline in the femoral sheath and intravenous tramadol). Tumor necrosis factor-α and visual analogue scale scores were evaluated immediately before the femoral nerve block and again at 4, 24, and 48 h after the femoral nerve block. All surgery was performed electively after 48 h of femoral nerve block.
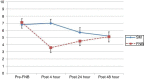
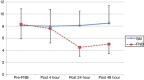
Results: The femoral nerve block group had a significantly lower mean tumor necrosis factor-α level at 24 (4.60 vs. 8.14, p < 0.001) and 48 h (5.05 vs. 8.56, p < 0.001) after the femoral nerve block, compared to the standard management group. The femoral nerve block group showed a significantly lower mean visual analogue scale score at 4 (3.63 vs. 7.06, p < 0.001) and 24 h (4.50 vs. 5.75, p < 0.001) after the femoral nerve block, compared to the standard management group.
Conclusions: Ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block using 0.3 mL.kg−1 of 0.5% bupivacaine up to a maximum of 20 mL resulted in a significant lower tumor necrosis factor-α level.
Keywords: Citocinas; Cytokines; Fator de necrose tumoral alfa; Femoral nerve; Fratura de quadril; Hip fracture; Inflammatory response; Nervo femoral; Resposta inflamatória; Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Copyright © 2018 Sociedade Brasileira de Anestesiologia. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fletcher A.K., Rigby A.S., Heyes F.L. Three-in-one femoral nerve block as analgesia for fractured neck of femur in the emergency department: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2003;41:227–233. - PubMed
-
- Beaudoin F.L., Haran J.P., Liebmann O. A comparison of ultrasound-guided three-in-one femoral nerve block versus parenteral opioids alone for analgesia in emergency department patients with hip fractures: a randomized controlled trial. Acad Emerg Med. 2013;20:584–591. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E.P., Kruse J.A., Jacobsen G., et al. The influence of early hemodynamic optimization on biomarker patterns of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2016–2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

