Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography: Variations of Liver Fibrosis Assessment as a Function of Depth, Force and Distance from Central Axis of the Transducer with a Comparison of Different Systems
- PMID: 30143339
- PMCID: PMC6594152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.07.003
Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography: Variations of Liver Fibrosis Assessment as a Function of Depth, Force and Distance from Central Axis of the Transducer with a Comparison of Different Systems
Abstract
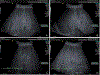
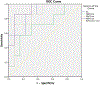
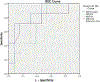
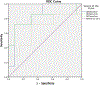
We evaluated variation in fibrosis staging caused by depth, pre-load force and measurement off-axis distance on different ultrasound shear wave elastography (SWE) systems prospectively in 20 patients with diffuse liver disease. Shear wave speed (SWS) was measured with transient elastography, acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) and 2-D shear wave elastography (SWE). ARFI and 2-D-SWE measurements were obtained at different depths (3, 5 and 7 cm), with different pre-load forces (4, 7 and 10N and variable) and at 0, 2 and 4cm off the central axis of the transducer. A single, blinded pathologist staged fibrosis using the METAVIR system (F0-F4). Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was charted to differentiate significant fibrosis (F ≥ 2). Depth was the only factor found to influence ARFI-derived values; no acquisition factors were found to affect 2-D-SWE SWS values. ARFI and 2-D-SWE for diagnosis of significant fibrosis at a depth of 7cm along the central axis had good diagnostic performance (areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve: 0.92 and 0.82, respectively), comparable to that of transient elastography. Further investigation of this finding will likely be of interest.
Keywords: Depth; Liver fibrosis; Off-axis; Pre-load force; Shear wave; Ultrasound elastography; Variation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography for Liver Disease. A Critical Appraisal of the Many Actors on the Stage.Ultraschall Med. 2016 Feb;37(1):1-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1567037. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Ultraschall Med. 2016. PMID: 26871407
-
Assessment of liver fibrosis with 2-D shear wave elastography in comparison to transient elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in patients with chronic liver disease.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Sep;41(9):2350-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26116161
-
Comparison of non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency using magnetic resonance elastography (MRE), acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) Quantification, and 2D-shear wave elastography (2D-SWE).PLoS One. 2018 Apr 26;13(4):e0196486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196486. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29698472 Free PMC article.
-
[SWE elastography in assessment of liver fibrosis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Feb 15;69:221-6. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1140338. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 25720608 Review. Polish.
-
Assessment of biopsy-proven liver fibrosis by two-dimensional shear wave elastography: An individual patient data-based meta-analysis.Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67(1):260-272. doi: 10.1002/hep.29179. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 28370257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance elastography and point-shear wave elastography for significant hepatic fibrosis screening: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 2;18(2):e0271572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271572. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36730265 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Shear Wave Elastography as a Non-invasive Biomarker of High-Risk Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Apr;46(4):972-980. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.12.020. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32005510 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the stiffness of normal cervix and its change with different factors using transvaginal two-dimensional shear wave elastography under strict quality control.BMC Med Imaging. 2023 May 22;23(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12880-023-01020-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37217872 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Dimensional Shear-Wave Elastography of the Thyroid in Clinically Healthy Dogs in Different Age Groups.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 22;14(11):1528. doi: 10.3390/ani14111528. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891575 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic accuracy of liver fibrosis in non-viral liver diseases using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 15;15(1):e0227358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227358. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31940395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Actis GC, Olivero A, Lagget M, Pellicano R, Smedile A, Rizzetto M. The practice of percutaneous liver biopsy in a gastrohepatology day hospital: a retrospective study on 835 biopsies. Dig Dis Sci 2007; 52:2576–9. - PubMed
-
- Barr RG, Ferraioli G, Palmeri ML, Goodman ZD, Garcia-Tsao G, Rubin J, Garra B, Myers RP, Wilson SR, Rubens D, Levine D. Elastography Assessment of Liver Fibrosis: Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference Statement. Radiology 2015; 276:845–61. - PubMed
-
- Barr RG, Zhang Z. Effects of precompression on elasticity imaging of the breast: development of a clinically useful semiquantitative method of precompression assessment. J Ultrasound Med 2012; 31:895–902. - PubMed
-
- Bedossa P, Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 1996; 24:289–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

