Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 represses diet-induced metabolic syndrome through AMPK activation
- PMID: 30143610
- PMCID: PMC6109074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05721-4
Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 represses diet-induced metabolic syndrome through AMPK activation
Abstract
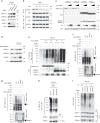
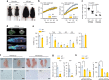
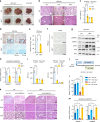
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a key role in controlling energy metabolism in response to physiological and nutritional status. Although AMPK activation has been proposed as a promising molecular target for treating obesity and its related comorbidities, the use of pharmacological AMPK activators has been met with contradictory therapeutic challenges. Here we show a regulatory mechanism for AMPK through its ubiquitination and degradation by the E3 ubiquitin ligase makorin ring finger protein 1 (MKRN1). MKRN1 depletion promotes glucose consumption and suppresses lipid accumulation due to AMPK stabilisation and activation. Accordingly, MKRN1-null mice show chronic AMPK activation in both liver and adipose tissue, resulting in significant suppression of diet-induced metabolic syndrome. We demonstrate also its therapeutic effect by administering shRNA targeting MKRN1 into obese mice that reverses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. We suggest that ubiquitin-dependent AMPK degradation represents a target therapeutic strategy for metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Attenuating MKRN1 E3 ligase-mediated AMPKα suppression increases tolerance against metabolic stresses in mice.Cell Stress. 2018 Oct 11;2(11):325-328. doi: 10.15698/cst2018.11.164. Cell Stress. 2018. PMID: 31225456 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Ebastine-mediated destabilization of E3 ligase MKRN1 protects against metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jan 31;82(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05535-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39888429 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuating MKRN1 E3 ligase-mediated AMPKα suppression increases tolerance against metabolic stresses in mice.Cell Stress. 2018 Oct 11;2(11):325-328. doi: 10.15698/cst2018.11.164. Cell Stress. 2018. PMID: 31225456 Free PMC article.
-
Acceleration of gastric tumorigenesis through MKRN1-mediated posttranslational regulation of p14ARF.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Nov 7;104(21):1660-72. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs424. Epub 2012 Oct 25. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 23104211 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Molecular Functions of RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligases from the MKRN Protein Family.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Sep;89(9):1558-1572. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924090037. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 39418515 Review.
-
Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders.Diabetes Metab. 2007 Dec;33(6):395-402. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.10.004. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Diabetes Metab. 2007. PMID: 17997341 Review.
Cited by
-
Makorin 1 Regulates Developmental Timing in Drosophila.Mol Cells. 2018 Dec 31;41(12):1024-1032. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0367. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 30396233 Free PMC article.
-
How to Inactivate Human Ubiquitin E3 Ligases by Mutation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 4;8:39. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00039. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32117970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary Conservation of MKRN3 and Other Makorins and Their Roles in Puberty Initiation and Endocrine Functions.Semin Reprod Med. 2019 Jul;37(4):166-173. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400965. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Semin Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 31972861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing to reveal non-parenchymal cell heterogeneity and immune network of acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Jul;97(7):1979-1995. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03513-4. Epub 2023 May 18. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37202523
-
Ubiquitination and Metabolic Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1466:47-79. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-7288-9_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39546135 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

