Genomic analysis reveals recurrent deletion of JAK-STAT signaling inhibitors HNRNPK and SOCS1 in mycosis fungoides
- PMID: 30144205
- PMCID: PMC6282857
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.22679
Genomic analysis reveals recurrent deletion of JAK-STAT signaling inhibitors HNRNPK and SOCS1 in mycosis fungoides
Abstract
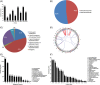
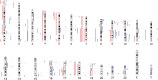
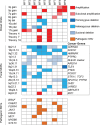
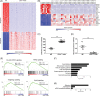
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Causative genetic alterations in MF are unknown. The low recurrence of pathogenic small-scale mutations (ie, nucleotide substitutions, indels) in the disease, calls for the study of additional aspects of MF genetics. Here, we investigated structural genomic alterations in tumor-stage MF by integrating whole-genome sequencing and RNA-sequencing. Multiple genes with roles in cell physiology (n = 113) and metabolism (n = 92) were found to be impacted by genomic rearrangements, including 47 genes currently implicated in cancer. Fusion transcripts involving genes of interest such as DOT1L, KDM6A, LIFR, TP53, and TP63 were also observed. Additionally, we identified recurrent deletions of genes involved in cell cycle control, chromatin regulation, the JAK-STAT pathway, and the PI-3-K pathway. Remarkably, many of these deletions result from genomic rearrangements. Deletion of tumor suppressors HNRNPK and SOCS1 were the most frequent genetic alterations in MF after deletion of CDKN2A. Notably, SOCS1 deletion could be detected in early-stage MF. In agreement with the observed genomic alterations, transcriptome analysis revealed up-regulation of the cell cycle, JAK-STAT, PI-3-K and developmental pathways. Our results position inactivation of HNRNPK and SOCS1 as potential driver events in MF development.
Keywords: JAK-STAT signaling; RNA sequencing; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; genomic rearrangements; mycosis fungoides; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2018 The Authors. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO‐EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768‐3785. - PubMed
-
- Nicolae‐Cristea AR, Benner MF, Zoutman WH, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of CDKN2A/CDKN2B deletions in patients with transformed mycosis fungoides and primary cutaneous CD30‐positive lymphoproliferative disease. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:784‐788. - PubMed
-
- Laharanne E, Chevret E, Idrissi Y, et al. CDKN2A‐CDKN2B deletion defines an aggressive subset of cutaneous T‐cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:547‐558. - PubMed
-
- van Doorn R, Dijkman R, Vermeer MH, Starink TM, Willemze R, Tensen CP. A novel splice variant of the Fas gene in patients with cutaneous T‐cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:5389‐5392. - PubMed
-
- van Doorn R, van Kester MS, Dijkman R, et al. Oncogenomic analysis of mycosis fungoides reveals major differences with Sezary syndrome. Blood. 2009;113:127‐136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

