Outbreaks of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella Choleraesuis in wild boars piglets from central-western Spain
- PMID: 30144295
- PMCID: PMC7168558
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.13003
Outbreaks of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella Choleraesuis in wild boars piglets from central-western Spain
Abstract
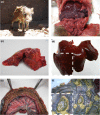
Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis is the aetiological agent of swine paratyphoid being a highly invasive zoonotic pathogen. Wild boar natural populations are experiencing a demographical expansion as well as some farms are breeding this species to release for hunting with management sometimes identical to that of domestic pigs, including supplementation, grouping, and antibiotic treatments. This situation increases the chance of contact between wild boars and livestock, and potentially induces stress, with different sanitary consequences. The present work aims to describe the clinical features of recent outbreaks caused by S. Choleraesuis in wild boar from central-western Spain, as well as the antimicrobial resistance and phylogenetic relationships of isolates involved. 28 strains of S. Choleraesuis were isolated from 28 different wild boars belonging to 10 different game states located in central western Spain and submitted to the Clinical Veterinary Hospital (CVH) of the University of Extremadura. Samples were taken from different organs and cultured according to the ISO 6579:2002 procedure. Suspicious colonies were identified by PCR and antimicrobial resistance was evaluated by disc diffusion susceptibility test and the presence of the main resistance genes as well as 18 plasmid replicons frequently found among the Enterobacteriaceae was verified by PCR. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis was applied to determine the genetic relationship between isolates. The outbreaks under study were characterized by high mortality (35%-84%) and a septicaemic presentation. S. Choleraesuis was isolated from all the wild boars analysed, and 26 of the 28 isolates presented resistance to at least one antibiotic. The predominant resistances found were against sulphonamide, streptomycin, tetracycline, and doxicicline and sul1, strA-strB, and tetA were the most prevalent resistance genes among isolates. 10 strains carried FIIA, FIB+H/1 or FIIA+H/1 plasmids. PFGE classified the isolates into four different profiles, grouped into two clusters. This results show that prevention against S. Choleraesuis must be considered in the sanitary programs of the wild boar breeders.
Keywords: Salmonella Choleraesuis; antibiotic resistance; epidemiology; wild boar.
© 2018 Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have read the manuscript and have approved this submission. All have made substantive contributions to this work. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissemination of antimicrobial-resistant isolates of Salmonella spp. in wild boars and its relationship with management practices.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022 Sep;69(5):e1488-e1502. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14480. Epub 2022 Mar 13. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022. PMID: 35182450 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolated from pigs in northern Italy.Res Vet Sci. 2025 Sep;193:105773. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2025.105773. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Res Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40570720
-
Prevalence of Salmonella spp. in tonsils, mandibular lymph nodes and faeces of wild boar from Spain and genetic relationship between isolates.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019 May;66(3):1218-1226. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13140. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019. PMID: 30720247
-
Phenotypic and genetic characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolates from humans and animals in Spain from 2006 to 2021.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024 Apr 2;79(4):790-800. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae029. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38366818 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella strains isolated from swine in Catalonia, Spain.Vet Rec. 2002 Feb 2;150(5):147-50. doi: 10.1136/vr.150.5.147. Vet Rec. 2002. PMID: 11873760 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial resistance in wild game mammals: a glimpse into the contamination of wild habitats in a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Jan 11;21(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04462-5. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 39799360 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of the Occurrence and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Foodborne Pathogens from Enterobacteriaceae in Wild Ungulates Within the European Countries.Pathogens. 2024 Nov 28;13(12):1046. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13121046. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39770307 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous D-ribose promotes gentamicin treatment of several drug-resistant Salmonella.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1053330. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1053330. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36419438 Free PMC article.
-
What WGS Reveals about Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica in Wildlife in Germany.Microorganisms. 2021 Sep 9;9(9):1911. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091911. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576806 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Occurrence of Staphylococcaceae with Reduced Susceptibility to Cefoxitin in Wild Ungulates in Brandenburg, Germany, Based on Land Use-Related Factors.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0256022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02560-22. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36169418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M. , Lertworapreecha, M. , Evans, M. C. , Bangtrakulnonth, A. , Chalermchaikit, T. , Hendriksen, R. S. , & Wegener, H. C. (2003). Antimicrobial susceptibility and occurrence of resistance genes among Salmonella enterica serovar Weltevreden from different countries. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 52(4), 715–718. - PubMed
-
- Allen, H. K. , Donato, J. , Wang, H. H. , Cloud‐Hansen, K. A. , Davies, J. , & Handelsman, J. (2010). Call of the wild: antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(4), 251–259. - PubMed
-
- Asai, T. , Namimatsu, T. , Osumi, T. , Kojima, A. , Harada, K. , Aoki, H. , & Takahashi, T. (2010). Molecular typing and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolates from diseased pigs in Japan. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 33(2), 109–119. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2008.08.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baskerville, A. , & Dow, C. (1973). Pathology of experimental pneumonia in pigs produced by Salmonella cholerae‐suis. Journal of Comparative Pathology, 83(2), 207–215. - PubMed
-
- Boitani, L. , & Mattei, L. (1992). Aging wild boar (Sus scrofa) by tooth eruption In Spitz F., Janeau G., Gonzalez G., & Aulagnier S. (Eds.), Ongulés/Ungulates. Société Française pour l’Étude et la Protection des Mammifères: Paris‐Toulouse.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

