Biomarkers of inflammation - LBP and TLR- predict progression of knee osteoarthritis in the DOXY clinical trial
- PMID: 30144513
- PMCID: PMC6263786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.08.005
Biomarkers of inflammation - LBP and TLR- predict progression of knee osteoarthritis in the DOXY clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate systemic inflammatory biomarkers in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) and their association with radiographic and biochemical OA progression.
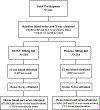
Methods: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding protein (LBP), soluble Toll-like receptor 4 (sTLR4) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were measured in plasma of 431 knee OA patients from the doxycycline (DOXY) trial at baseline and 18 months. Plasma lipopolysaccharide and lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) were also measured at 12 months. As a biochemical indicator of disease activity and OA progression, urinary (u) C-telopeptide of Type II collagen (uCTX-II) was measured in samples collected at baseline and 18 months. Change over 16 months in radiographic tibiofemoral joint space width (JSW in mm) and joint space narrowing (JSN≥0.5 mm) were used to indicate radiographic OA progression. Change over 18 months for uCTX-II was used as a secondary outcome. Both univariate and multivariable regression analyses were performed to test the association between Z-score transformed biomarkers and outcomes.
Results: Baseline LBP and time-integrated concentration (TIC) of LBP over 12 and 18 months were associated with worsening joint space width (JSW) (parameter estimates: -0.1 to -0.07) and JSN (OR: 1.32 to 1.42) adjusting for treatment group, age, body mass index (BMI) and corresponding baseline radiographic measures. Baseline sTLR4 and TIC over 18 months were associated with change in uCTX-II over 18 months (adjusted parameter estimates: 0.0017 to 0.0020). Results were not modified by treatment with doxycycline.
Conclusion: Plasma LBP and sTLR4 were associated with knee OA progression over 16-18 months. These results lend further support for a role of systemic low-grade inflammation in the pathogenesis of knee OA progression.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Inflammation; Knee osteoarthritis; LBP; Path analysis; sTLR4.
Copyright © 2018 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors have competing interests to disclose. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Symmons DMC, Pfleger B Global burden of osteoarthritis in the year 2000. WHO; [online], www.who.int/entity/healthinfo/statistics/bod_osteoarthritis.pdf 2003.
-
- Sellam J, Berenbaum F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2010;6(11):625–35. - PubMed
-
- Pessler F, Dai L, Diaz-Torne C, et al. The synovitis of “non-inflammatory” orthopaedic arthropathies: a quantitative histological and immunohistochemical analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67(8):1184–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

