Diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson's disease at a glance: where are we?
- PMID: 30145631
- PMCID: PMC6132920
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-018-1910-4
Diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson's disease at a glance: where are we?
Abstract
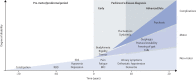
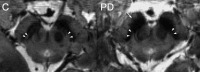
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder whose aetiology remains unclear: degeneration involves several neurotransmission systems, resulting in a heterogeneous disease characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms. PD causes progressive disability that responds only to symptomatic therapies. Future advances include neuroprotective strategies for use in at-risk populations before the clinical onset of disease, hence the continuing need to identify reliable biomarkers that can facilitate the clinical diagnosis of PD. In this evaluative review, we summarize information on potential diagnostic biomarkers for use in the clinical and preclinical stages of PD.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diagnosis; Parkinson’s disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, White LR, et al. Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2001;57:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Abbott RD, Ross GW, White LR, et al. Excessive daytime sleepiness and subsequent development of Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2005;65:1442–1446. - PubMed
-
- Abd-Elhadi S, Basora M, Vilas D, et al. Total α-synuclein levels in human blood cells, CSF, and saliva determined by a lipid-ELISA. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:7669–7677. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qassabi A, Fereshtehnejad S-M, Postuma RB. Sleep disturbances in the prodromal stage of Parkinson disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017;19:22. - PubMed
-
- Andersen AD, Binzer M, Stenager E, Gramsbergen JB. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease—a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

