Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015
- PMID: 30146071
- PMCID: PMC6719291
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2019 Oct;119(10):1759. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.07.025. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2019. PMID: 31444138 No abstract available.
Abstract
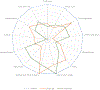
The Healthy Eating Index (HEI) is a measure for assessing whether a set of foods aligns with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA). An updated HEI is released to correspond to each new edition of the DGA, and this article introduces the latest version, which reflects the 2015-2020 DGA. The HEI-2015 components are the same as in the HEI-2010, except Saturated Fat and Added Sugars replace Empty Calories, with the result being 13 components. The 2015-2020 DGA include explicit recommendations to limit intakes of both Added Sugars and Saturated Fats to <10% of energy. HEI-2015 does not account for excessive energy from alcohol within a separate component, but continues to account for all energy from alcohol within total energy (the denominator for most components). All other components remain the same as for HEI-2010, except for a change in the allocation of legumes. Previous versions of the HEI accounted for legumes in either the two vegetable or the two protein foods components, whereas HEI-2015 counts legumes toward all four components. Weighting approaches are similar to those of previous versions, and scoring standards were maintained, refined, or developed to increase consistency across components; better ensure face validity; follow precedent; cover a range of intakes; and, when applicable, ensure the DGA level corresponds to a score >7 out of 10. HEI-2015 component scores can be examined collectively using radar graphs to reveal a pattern of diet quality and summed to represent overall diet quality.
Keywords: Diet indexes; Diet quality; Dietary intake; Dietary patterns; Healthy Eating Index.
Copyright © 2018 Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
STATEMENT OF POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



References
-
- Nutrition and Your Health: 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th edition Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office; 2015.
-
- Guenther PM, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM. Development of the Healthy Eating Index-2005. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(11):1896–1901. - PubMed
-
- Schap T, Kuczynski K, Hiza H. Healthy Eating Index-beyond the score. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117(4):519–521. - PubMed
-
- Onvani S, Haghighatdoost F, Surkan PJ, Larijani B, Azadbakht L Adherence to the Healthy Eating Index and Alternative Healthy Eating Index dietary patterns and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies.J Hum Nutr Diet 2017;30(2):216–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

