A miRNA Panel Predicts Sensitivity of FGFR Inhibitor in Lung Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 30146263
- PMCID: PMC6339511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.06.004
A miRNA Panel Predicts Sensitivity of FGFR Inhibitor in Lung Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
Purpose: To test whether a microRNA (miRNA) panel may serve as an alternative biomarker of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor sensitivity in lung cancer.
Methods: Histologically diverse lung cancer cell lines were submitted to assays for ponatinib and AZD4547 sensitivity. miRNAs, FGFR1 messenger RNA, gene copy number, and protein expression were detected by real-time quantitative PCR, fluorescence in-situ hybridization, and immunoblotting in 34 lung cancer cell lines.
Results: Among 34 cell lines, 14 exhibited ponatinib sensitivity and 20 exhibited AZD4547 sensitivity (drug concentration causing 50% inhibition values < 100 nmol/L). A total of 39 of the 377-miRNA set were initially identified from the 4 paired ponatinib-sensitive or -insensitive cell lines to have at least an 8-fold differential expression and then were detected in all the 34 cell lines. A predictive panel of 3 miRNAs (let-7c, miRNA155, and miRNA218) was developed that had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.886 with a sensitivity of 71.4% and specificity of 77.3% to predict response to ponatinib. The miRNA panel performed similar to FGFR1 protein expression (AUC = 0.864) and messenger RNA expression (AUC = 0.939), and better than FGFR1 amplification (AUC = 0.696). Furthermore, we validated this panel using data for sensitivity to AZD4547 in the cell line cohort with an AUC of 0.931 and a sensitivity of 73.3% and specificity of 76.2%, respectively.
Conclusion: The developed miRNA panel (let-7c, miRNA155, and miRNA218) may be useful in predicting response to FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, either ponatinib or AZD4547 in lung cancer cell lines, and warrants further validation in the clinical setting.
Keywords: AZD4547; biomarker; lung cancer; miRNA; ponatinib.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
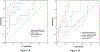
Similar articles
-
Translating the therapeutic potential of AZD4547 in FGFR1-amplified non-small cell lung cancer through the use of patient-derived tumor xenograft models.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 15;18(24):6658-67. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2694. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23082000
-
FGFR1 mRNA and protein expression, not gene copy number, predict FGFR TKI sensitivity across all lung cancer histologies.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 15;20(12):3299-309. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3060. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24771645 Free PMC article.
-
Novel FGFR inhibitor ponatinib suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells overexpressing FGFR1.Oncol Rep. 2013 Jun;29(6):2181-90. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2386. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23563700
-
Implications of MicroRNAs in the Treatment of Gefitinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 15;17(2):237. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020237. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26891293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical implication of microrna for lung cancer.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013 May;28(4):261-7. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1401. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 23496233 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering role of FGFR signalling pathway in pancreatic cancer.Cell Prolif. 2019 May;52(3):e12605. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12605. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30945363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGFR1Pred: an artificial intelligence-based model for predicting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug;28(4):2065-2076. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10714-7. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 37566198
-
Targeting the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor (FGFR) Family in Lung Cancer.Cells. 2021 May 10;10(5):1154. doi: 10.3390/cells10051154. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas12a-coupled multiplexed strand displacement amplification for miRNA155 one-tube detection: via a dual-cavity PCR tube.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Jul 18;191(8):470. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06538-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39023769
References
-
- Jiang T, Gao G, Fan G, et al. FGFR1 amplification in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2015. January;87(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Desai A, Adjei AA .FGFR Signaling as a Target for Lung Cancer Therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2016. January;11(1):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Gozgit JM, Wong MJ, Moran L, et al. Ponatinib (AP24534), a multitargeted pan-FGFR inhibitor with activity in multiple FGFR-amplified or mutated cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. March;11(3):690–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

