SIRT1 Activation Disrupts Maintenance of Myelodysplastic Syndrome Stem and Progenitor Cells by Restoring TET2 Function
- PMID: 30146412
- PMCID: PMC6143172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.07.018
SIRT1 Activation Disrupts Maintenance of Myelodysplastic Syndrome Stem and Progenitor Cells by Restoring TET2 Function
Abstract
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a largely incurable hematological malignancy, is derived from aberrant clonal hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) that persist after conventional therapies. Defining the mechanisms underlying MDS HSPC maintenance is critical for developing MDS therapy. The deacetylase SIRT1 regulates stem cell proliferation, survival, and self-renewal by deacetylating downstream proteins. Here we show that SIRT1 protein levels were downregulated in MDS HSPCs. Genetic or pharmacological activation of SIRT1 inhibited MDS HSPC functions, whereas SIRT1 deficiency enhanced MDS HSPC self-renewal. Mechanistically, the inhibitory effects of SIRT1 were dependent on TET2, a safeguard against HSPC transformation. SIRT1 deacetylated TET2 at conserved lysine residues in its catalytic domain, enhancing TET2 activity. Our genome-wide analysis identified cancer-related genes regulated by the SIRT1/TET2 axis. SIRT1 activation also inhibited functions of MDS HSPCs from patients with TET2 heterozygous mutations. Altogether, our results indicate that restoring TET2 function through SIRT1 activation represents a promising means to target MDS HSPCs.
Keywords: HSPCs; SIRT1; SRT1720; TET2; acetylation; myelodysplastic syndrome.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

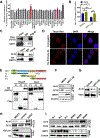
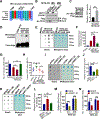

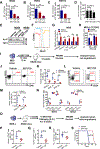
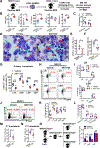
Comment in
-
Revert the SIRT: Normalizing SIRT1 Activity in Myelodysplastic Stem Cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Sep 6;23(3):315-317. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.08.003. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30193128
References
-
- Aslanyan MG, Kroeze LI, Langemeijer SM, Koorenhof-Scheele TN, Massop M, van Hoogen P, Stevens-Linders E, van de Locht LT, Tonnissen E, van der Heijden A, et al. (2014). Clinical and biological impact of TET2 mutations and expression in younger adult AML patients treated within the EOrTc/GIMEMA AML-12 clinical trial. Annals of hematology 93, 1401–1412. - PubMed
-
- Baksi A, Kraydashenko O, Zalevkaya A, Stets R, Elliott P, Haddad J, Hoffmann E, Vlasuk GP, and Jacobson EW (2014). A phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled, doubleblind, multi-dose study of SRT2104, a SIRT1 activator, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. British journal of clinical pharmacology 78, 69–77. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

