Insertion element mediated mgrB disruption and presence of ISKpn28 in colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 30147346
- PMCID: PMC6101004
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S161146
Insertion element mediated mgrB disruption and presence of ISKpn28 in colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: In Klebsiella pneumoniae, mgrB and components of pmrHFIJKLM operon play a major role in colistin resistance.
Methods: We analyzed 23 nonduplicating colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates, collected during the years 2011-2015, for the possible mechanism underlying their nonsusceptibility to colistin. Isolates were tested for their minimum inhibitory concentrations and antibiotic resistance determinants and genotyped by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). The MLST genes, antibiotic-resistant genes, and the genes of two component system (TCS), including mgrB, PhoQ/PhoP, pmrA/B, and CrrAB, were investigated by PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing.
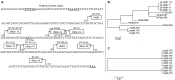
Results: All isolates were distributed in eight sequence types (STs) and showed mutations either in mgrB or PhoP genes. ISKpn14 was found in 10, ISKpn28 in four, and IS903 in three isolates. One isolate showed deletion of a single nucleotide in mgrB open reading frame causing premature stop codon. L26Q substitution in PhoP was found in five isolates.
Conclusion: The mutations in mgrB were mostly mediated by insertion elements (IS). ISKpn14 is the major IS while ISKpn28 is reported for the first time in mediating mgrB disruption. IS903, an IS5 family member, involved in mgrB disruption in three ST-152 NDM-1-positive isolates, was previously responsible for omp-36 disruption in our carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae and appears to contribute to transform the isolates into a pan-drug ones. Also, the abundance of insertion sites in mgrB indicates the plasticity of this gene. In our isolates, IS-mediated colistin resistance appears to be a later phenomenon than mutation in PhoP gene.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; colistin resistance; insertion elements; mgrB gene mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Mutated Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 2;7(12):414. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7120414. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36548669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the ISKpn element in mediating mgrB gene mutations in ST11 hypervirulent colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1277320. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277320. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37840706 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of different colistin resistance mechanisms among multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Bulgaria.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2022 Jun 27;69(3):220-227. doi: 10.1556/030.2022.01746. Print 2022 Sep 16. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2022. PMID: 35895482
-
Colistin resistance due to insertional inactivation of the mgrB in Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin: First report from India.Rev Esp Quimioter. 2018 Oct;31(5):406-410. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2018. PMID: 30221899 Free PMC article.
-
Global prevalence of mutation in the mgrB gene among clinical isolates of colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1386478. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1386478. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38912352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rapid Emergence of a Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Isolate in an Inpatient in a Teaching Hospital in China After Treatment with Multiple Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Mar 10;13:799-804. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S243334. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32210594 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Plasmids and Genes from Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(11):1627. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111627. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421271 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Mutated Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Dec 2;7(12):414. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7120414. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36548669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A census of anti-CRISPR proteins reveals AcrIE9 as an inhibitor of Escherichia coli K12 Type IE CRISPR-Cas system.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 10:2025.05.07.652737. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.07.652737. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654865 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Identification of mcr-8 in Clinical Isolates From Qatar and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Profiles.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 24;11:1954. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01954. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32983006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olaitan AO, Diene SM, Kempf M, et al. Worldwide emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy humans and patients in Lao PDR, Thailand, Israel, Nigeria and France owing to inactivation of the PhoP/PhoQ regulator mgrB: an epidemiological and molecular study. Int JAntimicrob Agents. 2014;44(6):500–507. - PubMed
-
- CLSI Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twentieth Informational Supplement. 2010 M100-S20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

