Clinical value of circulating ESR1 mutations for patients with metastatic breast cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 30147360
- PMCID: PMC6097501
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S173193
Clinical value of circulating ESR1 mutations for patients with metastatic breast cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The clinical implication of plasma ESR1 mutations in the estrogen receptor (ER)-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients who had progressed after prior aromatase inhibitor (AI)-based therapy remains controversial. We conducted the first meta-analysis to investigate the prognostic significance and predictive role of plasma ESR1 mutations in MBC patients with prior exposure to AI therapy.
Materials and methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for eligible studies. Meta-analysis was conducted to calculate combined hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Subgroup and sensitivity analyses were also performed.
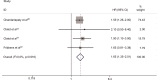
Results: This study enrolled a total of 1,530 patients with ER-positive MBC cases from six articles, including 429 ESR1 mutation carriers (28.04%). Meta-analysis demonstrated that plasma ESR1 mutation carriers had significantly worse PFS (HR: 1.40, 95% CI: 1.17-1.66; P<0.0001) and OS (HR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.36-2.01; P<0.0001) compared to wild-type ESR1. Subgroup analysis showed that plasma ESR1 mutations were associated with shorter PFS after AI-based treatment, but were not significantly predictive of outcome on fulvestrant-containing therapy (HR: 1.26, 95% CI: 0.98-1.62; P=0.077). As for different ESR1 mutations, D538G mutation implied significantly worse PFS (HR: 1.50, 95% CI: 1.18-1.91; P=0.01), while Y537S mutation was not correlated with PFS (HR: 1.65, 95% CI: 0.87-1.73; P=0.134).
Conclusion: The meta-analysis indicated that plasma ESR1 mutation assessment may have prognostic significance and clinical value in guiding further endocrine therapy choice in ER+ MBC patients who received prior AI therapy.
Keywords: ESR1 mutations; breast carcinoma; cfDNA; ctDNA; meta analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Smith IE, Dowsett M. Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(24):2431–2442. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG): Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

