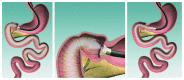
The EndoBarrier: Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner for Diabetes and Weight Loss
- PMID: 30147720
- PMCID: PMC6083488
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7823182
The EndoBarrier: Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Liner for Diabetes and Weight Loss
Abstract
The rapid rise of obesity and type 2 diabetes poses a global threat to healthcare and is a major cause of mortality and morbidity. Bariatric surgery has revolutionised the treatment of both these conditions but is invasive and associated with an increased risk of complications. The EndoBarrier is a device placed endoscopically in the duodenum, which is designed to mimic the effects of gastric bypass surgery with the aim of inducing weight loss and improving glycaemic control. This review outlines the current clinical evidence of the device, its efficacy, potential mechanisms of action, and utility in clinical practice.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Obesity and overweight factsheet. 2018. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- WHO. Global Report on Diabetes. 2016 http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/
-
- Koehestanie P., de Jonge C., Berends F. J., Janssen I. M., Bouvy N. D., Greve J. W. M. The effect of the endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Annals of Surgery. 2014;260(6):984–992. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000794. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources