No Performance or Affective Advantage of Drinking versus Rinsing with Water during a 15-km Running Session in Female Runners
- PMID: 30147823
- PMCID: PMC6102191
- DOI: 10.70252/ZUUG4953
No Performance or Affective Advantage of Drinking versus Rinsing with Water during a 15-km Running Session in Female Runners
Abstract
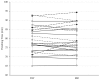
The advantage of ingesting fluids during endurance exercise lasting < 90 min has recently been challenged, but literature confirming or disputing this case is limited, particularly for female athletes. This study examined the effects of consuming water versus mouth rinsing with water during a running time trial. Recreationally active female runners (n = 19) completed two, 15-km time trials on an outdoor course in temperate environment (~20ºC; 87% RH) separated by at least one week in a randomized cross-over study design. Participants consumed 355 ml of water (DW) during their run or mouth rinsed (MR) with water from a handheld water bottle every 3 km for 5 s with physiological, perceptual, and affective variables assessed. DW or MR did not affect completion time (79.8 ± 8.1 min and 79.2 ± 8.2 min, p = 0.23), HR (p = 0.35), or RPE (p = 0.73), respectively. Sweat losses were greater (p = 0.03) for DW: 1.47 ± 0.34 L compared to MR: 1.28 ± 0.27 L; however, thirst sensation was not significantly different for MR: 6.7 ± 1.4 compared to DW: 6.2 ± 1.6. A significant effect was exhibited for time (p < 0.01) but not condition for Feeling Scale and Felt Arousal Scale or Energetic and Tense Arousal. Carrying only one smaller fluid container for MR versus a larger or multiple water bottles/backpack systems used for water consumption can reduce fluid load carried during extended duration runs without altering performance or affect for runs of 1.0-1.5 h. MR may also be beneficial to decrease thirst without ingesting fluid for runners that limit exercise fluid consumption because of gastrointestinal discomfort concerns.
Keywords: Hydration; affect; endurance performance; perceived exertion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Optimal Weight Carriage System for Runners: Comparison Between Handheld Water Bottles, Waist Belts, and Backpacks.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 30;11:571221. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.571221. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33117192 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of mouth rinsing and ingestion of carbohydrate solutions on mood and perceptual responses during exercise.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017 Jan 25;14:4. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0161-8. eCollection 2017. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28138315 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acute Caffeine Mouth Rinse Does Not Change the Hydration Status following a 10 km Run in Recreationally Trained Runners.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 6;2020:6598753. doi: 10.1155/2020/6598753. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596348 Free PMC article.
-
Sweat rate and fluid turnover in American football players compared with runners in a hot and humid environment.Br J Sports Med. 2005 Apr;39(4):205-11; discussion 205-11. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2004.011767. Br J Sports Med. 2005. PMID: 15793087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What do athletes drink during competitive sporting activities?Sports Med. 2013 Jul;43(7):539-64. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0028-y. Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23529286 Review.
Cited by
-
Rating of perceived exertion in continuous sports: a scoping review with evidence gap map.Front Sports Act Living. 2025 Jul 15;7:1553998. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1553998. eCollection 2025. Front Sports Act Living. 2025. PMID: 40735419 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Exercise Sweat Loss Estimation Accuracy of Athletes and Physically Active Adults: A Review.Sports (Basel). 2020 Aug 11;8(8):113. doi: 10.3390/sports8080113. Sports (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32796724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic narrative review of extrinsic strategies to improve affective responses to exercise.Front Sports Act Living. 2023 Jul 11;5:1186986. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2023.1186986. eCollection 2023. Front Sports Act Living. 2023. PMID: 37496882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong L, Maresh C, Castellani J, Bergeron M, Kenefick R, LaGrasse K, et al. Urinary indicies of hydration status. Int J Sport Nutr. 1994;4(3):265–279. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong LE, Casa DJ, Emmanuel H, Ganio MS, Klau JF, Lee EC, et al. Nutritional, Physiological, and Perceptual Responses During a Summer Ultraendurance Cycling Event. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(2):307–318. - PubMed
-
- Arnaoutis G, Kavouras SA, Christaki I, Sidossis LS. Water Ingestion Improves Performance Compared with Mouth Rinse in Dehydrated Subjects. Med Sci Sport Exerc. 2012;44(1):175–179. - PubMed
-
- Backhouse SH, Biddle SJH, Williams C. The influence of water ingestion during prolonged exercise on affect. Appetite. 2007;48(2):193–198. - PubMed
-
- Beelen M, Berghuis J, Bonaparte B, Ballak SB, Jeukendrup AE, van Loon LJC. Carbohydrate mouth rinsing in the fed state: lack of enhancement of time-trial performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2009;19(4):400–409. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
