Pancreatic, periampullary and biliary cancer with liver metastases: Should we consider resection in selected cases?
- PMID: 30147847
- PMCID: PMC6107475
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i8.211
Pancreatic, periampullary and biliary cancer with liver metastases: Should we consider resection in selected cases?
Abstract
Aim: To analyse the safety and efficacy of curative intent surgery in biliary and pancreatic cancer.
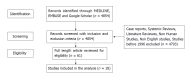
Methods: An extensive literature review was performed using MEDLINE, Google Scholar and EMBASE to identify articles regarding hepato-pancreatoduodenectomy or resection of liver metastasis in patients with pancreatic, biliary tract, periampullary and gallbladder cancers.
Results: A total of 19 studies were identified and reviewed. Major hepatectomy was undertaken in 391 patients. The median overall survival for pancreatic cancer ranged from 5-36 mo and for biliary tract/gallbladder cancer, it was 8-38 mo. The 30 d mortality rate was only 1%-9%. Overall Survival was significantly better for patients, who had good response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, underwent metachronous liver resection and who had intestinal type tumours.
Conclusion: Resection of liver metastases in pancreatic and biliary cancers may provide survival benefit without compromising safety and quality of life in a very select group of patients. These data may be utilised to formulate selection criteria that may allow future investigation of resection in the era of more effective systemic therapy.
Keywords: Cholangiocarcinoma; Gall bladder; Liver resection; Pancreas; Review.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have nothing to disclose.
References
-
- Belghiti J, Hiramatsu K, Benoist S, Massault P, Sauvanet A, Farges O. Seven hundred forty-seven hepatectomies in the 1990s: an update to evaluate the actual risk of liver resection. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;191:38–46. - PubMed
-
- Aloia TA, Vauthey JN, Loyer EM, Ribero D, Pawlik TM, Wei SH, Curley SA, Zorzi D, Abdalla EK. Solitary colorectal liver metastasis: resection determines outcome. Arch Surg. 2006;141:460–466; discussion 466-467. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources