Use of erbium laser in the treatment of persistent post-radiotherapy laryngeal edema: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 30149805
- PMCID: PMC6112140
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1480-9
Use of erbium laser in the treatment of persistent post-radiotherapy laryngeal edema: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Post-radiotherapy laryngeal edema may affect the patients' quality of life, leading to repeated treatment attempts, which include massage/physical therapy, inhalations, and/or tracheostomy.
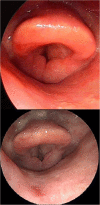
Case presentation: We report the surgical treatment approach of a 69-year-old patient with severe persistent post-radiotherapy laryngeal edema. After multiple inpatient admissions and failed conservative therapy, we used the erbium laser to treat the arytenoid edema. After repeated procedures, no complications were observed. The patient remained free of symptoms after 30 months of follow-up.
Conclusions: The authors provide an easy-to-perform, safe, and quick surgical technique without non-severe or severe complications. Using this technique repeatedly, complications from excessive thermal damage with CO2 laser or unpleasant solutions such as tracheostomy can be avoided.
Keywords: Edema; Erbium; Laryngeal; Laser microsurgery; Post-radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Obtained
Competing interests
Both authors declare that they do have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Bertrand MF, Semez G, Leforestier E, Muller-Bolla M, Nammour S, Rocca JP. Er:YAG laser cavity preparation and composite resin bonding with a single-component adhesive system: relationship between shear bond strength and microleakage. Lasers Surg Med. 2006;38(6):615–623. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20342. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Greene D, Egbert BM, Utley DS, Koch RJ. In vivo model of histologic changes after treatment with the superpulsed CO (2) laser, erbium:YAG laser, and blended lasers: a 4- to 6-month prospective histologic and clinical study. Lasers Surg Med. 2000;27(4):362–372. doi: 10.1002/1096-9101(2000)27:4<362::AID-LSM10>3.0.CO;2-H. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herdman RC, Charlton A, Hinton AE, Freemont AJ. An in vitro comparison of the erbium: YAG laser and the carbon dioxide laser in laryngeal surgery. J Laryngol Otol. 1993;107(10):908–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

