Changing Patterns of Contraceptive Use and the Decline in Rates of Pregnancy and Birth Among U.S. Adolescents, 2007-2014
- PMID: 30149926
- PMCID: PMC6423509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.05.017
Changing Patterns of Contraceptive Use and the Decline in Rates of Pregnancy and Birth Among U.S. Adolescents, 2007-2014
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the influence of sexual activity and contraceptive use on the decline in adolescent birth rates and pregnancy rates since 2007.
Methods: We estimated trends in pregnancy risk from 2007 to 2014 using national data on behaviors of women aged 15-19.
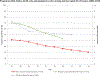
Results: In 2007-2014, increases occurred in use of one or more contraceptive methods at last sex (78%-88%), dual method use (24%-33%), long-acting reversible contraception including intrauterine device and implant (1%-7%), withdrawal (15%-26%), and withdrawal in combination with other methods (7%-17%). Pill use rose and then fell over time. Level of sexual activity did not change over time. The decline in pregnancy risk among women aged 15-19 was entirely attributable to improvements in contraceptive use.
Conclusions: Improvements in contraceptive use-including increases in use of long-acting reversible contraception and withdrawal in combination with another method-appear to be driving recent declines in adolescent birth and pregnancy rates.
Keywords: Abstinence; Adolescent pregnancy; Birthrate; Contraception; Sexual behaviors.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kost K, Maddow-Zimet I, Arpaia A. Pregnancies, births and abortions among adolescents and young women in the United States, 2013: National and State Trends by Age, Race and Ethnicity. 2017.
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJK, Driscoll AK, Drake P. Births: Final data for 2016. Natl Vital Stat Rep Cent Dis Control Prev Natl Cent Health Stat Natl Vital StatSyst 2018;67:55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical