Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of Eravacycline
- PMID: 30150464
- PMCID: PMC6201080
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01174-18
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies of the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of Eravacycline
Abstract
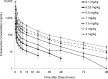
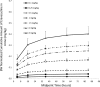
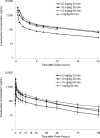
Eravacycline is a novel, fully synthetic fluorocycline antibiotic with in vitro activity against aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens, including multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. The pharmacokinetics (PK), urinary excretion, and safety/tolerability of intravenous (i.v.) eravacycline were evaluated in single- and multiple-ascending-dose studies. Healthy subjects received single i.v. doses of 0.1 to 3 mg/kg of body weight or 10 days of treatment with 0.5 or 1.5 mg/kg every 24 h (q24h) over 30 min, 1.5 mg/kg q24h over 60 min, or 1 mg/kg q12h over 60 min. After single doses, total exposure (the area under the plasma concentration-time curve [AUC]) and the maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) of eravacycline increased in an approximately dose-proportional manner. After multiple doses, steady state was achieved within 5 to 7 days. Accumulation ranged from approximately 7% to 38% with the q24h dosing regimens and was 45% with 1 mg/kg q12h. Eravacycline was generally well tolerated, with dose-related nausea, infusion site effects, and superficial phlebitis that were mild or moderate occurring. These results provide support for the 1-mg/kg q12h regimen used in clinical studies of eravacycline.
Keywords: eravacycline; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2018 Newman et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eravacycline: A Review in Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):315-324. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01067-3. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30783960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Eravacycline, a Novel Fluorocycline Antibacterial Agent.Drugs. 2016 Apr;76(5):567-88. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0545-8. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26863149 Review.
-
Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Eravacycline vs Ertapenem in Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections in the Investigating Gram-Negative Infections Treated With Eravacycline (IGNITE 1) Trial: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Surg. 2017 Mar 1;152(3):224-232. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.4237. JAMA Surg. 2017. PMID: 27851857 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 2, randomized, double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of two dose regimens of eravacycline versus ertapenem for adult community-acquired complicated intra-abdominal infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(4):1847-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01614-13. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24342651 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Comprehensive Analysis of the Tissue Distribution of Eravacycline in Rabbits.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Aug 27;62(9):e00275-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00275-18. Print 2018 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29941646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
First-in-human study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target attainment analysis of FL058 alone and in combination with meropenem in healthy subjects.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Jan 10;68(1):e0133023. doi: 10.1128/aac.01330-23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38054726 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of eravacycline and comparator agents against bacterial pathogens isolated from patients with cancer.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023 Mar 2;5(2):dlad020. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad020. eCollection 2023 Apr. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 36875177 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Antimicrobial Activity and Dose Optimization of Eravacycline and Other Tetracycline Derivatives Against Levofloxacin-Non-Susceptible and/or Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Sep 8;16:6005-6015. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S425061. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37705512 Free PMC article.
-
Eravacycline: A Review in Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):315-324. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01067-3. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30783960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass Balance and Drug Interaction Potential of Intravenous Eravacycline Administered to Healthy Subjects.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Feb 26;63(3):e01810-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01810-18. Print 2019 Mar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30559132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson JR, Porter SB, Johnston BD, Thuras P. 2015. Activity of eravacycline against Escherichia coli clinical isolates collected from U.S. veterans in 2011 in relation to coresistance phenotype and sequence type 131 genotype. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:1888–1891. doi:10.1128/AAC.02403-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

