Targeting TGF-β Signaling in Kidney Fibrosis
- PMID: 30150520
- PMCID: PMC6165001
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092532
Targeting TGF-β Signaling in Kidney Fibrosis
Abstract
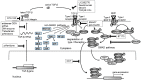
Renal fibrosis is the final common pathway of numerous progressive kidney diseases, and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) has an important role in tissue fibrosis by up-regulating matrix protein synthesis, inhibiting matrix degradation, and altering cell-cell interaction. Many strategies targeting TGF-β, including inhibition of production, activation, binding to the receptor, and intracellular signaling, have been developed. Some of them were examined in clinical studies against kidney fibrosis, and some are applied to other fibrotic diseases or cancer. Here, I review the approaches targeting TGF-β signaling in kidney fibrosis.
Keywords: antisense; galunisertib; gene therapy; glomerulosclerosis; interstitial fibrosis; ligand trap; pirfenidone; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Border W., Noble N. Transforming growth factor in tissue fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331:1286–1292. - PubMed
-
- Okuda S., Languino L.R., Ruoslahti E., Border W.A. Elevated expression of transforming growth factor-β and proteoglycan production in experimental glomerulonephritis. Possible role in expansion of the mesangial extracellular matrix. J. Clin. Investig. 1990;86:4534–4562. doi: 10.1172/JCI114731. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kagami S., Border W.A., Ruoslahti E., Noble N.A. Coordinated expression of β1 integrins and transforming growth factor-β-induced matrix proteins in glomerulonephritis. Lab. Investig. 1993;69:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Wu C.F., Chiang W.C., Lai C.F., Chang F.C., Chen Y.T., Chou Y.H., Wu T.H., Linn G.R., Ling H., Wu K.-D., et al. Transforming growth factor β-1 stimulates profibrotic epithelial signaling to activate pericyte-myofibroblast transition in obstructive kidney fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013;182:118–131. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

